|

With the upcoming monsoon rains:
Be alert to prevent Dengue
By Manjula FERNANDO
'Dengue fever' can raise its ugly head again with the upcoming
monsoon rains,Health authorities issued this warning last week.
It would be timely to remind residents how deadly the disease could
become and educate them of the importance of personal vigil and
individual contribution on Dengue control.
 By March and April every year the mosquitoes almost vanish, then
people are quite relaxed during this period. Even 'fogging' and other
mosquito control activities by the Colombo Municipal Council (CMC) takes
a breathing space in March and April. By March and April every year the mosquitoes almost vanish, then
people are quite relaxed during this period. Even 'fogging' and other
mosquito control activities by the Colombo Municipal Council (CMC) takes
a breathing space in March and April.
But once May approaches the problem raises its ugly head again.
Hence, notwithstanding the usual trends, we must have a consistent
program right throughout the year so as to fight this menace
effectively.
Dengue Fever comes in two types. The mild Dengue Fever DF and the
fatal Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, commonly known among the medical
practitioners by the abbreviation DHF.
Patients with ordinary Dengue fever will undergo a 'Feverish Phase'
and the 'Recovery Phase' and get cured without suffering any
complications. Some people with DF may not even develop a significantly
high temperature. About half of the DF patients record platelet counts
below 100,000.
In DHF there is a fatal critical phase in between the feverish phase
and the recovery phase. The number of patients who suffer DHF is about
100 out of 10,000 dengue patients. DHF patients have their platelet
counts dropping below 100,000. This should not be cause for panic.
The critical phase of DHF has to be managed with extreme caution.
This is the phase the patients could die due to 'shock' if inadequate
fluid is given to them. Nevertheless, too much fluid could also cause
death.
Too much fluid during this critical phase of the disease can result
in fluid overload.
During the critical phase that can develop within the 3rd to 7th day
of the onset of fever, the patients start plasma (the fluid in the
blood) leakage through the tiny blood vessels. This phase lasts for
about 48 hours.
During the height of the leakage (after first 24 hours), the patients
could completely leak one bottle of ordinary saline into his abdominal
or chest cavities within 1-2 hours.
As a result he would develop breathing difficulties due to fluid in
the lungs.
Clinical administration of fluid is needed to retain the lost fluid
in a DHF patient who develops plasma leakage, in order to prevent them
going into 'shock'. Shock is one of the two reasons for death in Dengue
Fever. But during the 48 hour 'critical phase' the IV administration
should be done with extreme care and strict supervision of a skilled
medical practitioner.
The Health Ministry has brought down a special Intravenous fluid
Dextran 40 to treat patients in this critical phase.
This drug which is similar to 'Saline' does not seep through as
easily as Saline.
Therefore the drug can minimize fatalities caused by 'fluid overload'
- the second cause of death in Dengue. Dengue deaths can be minimized if
the patient and the condition is properly managed during the critical
stage of the disease.
Tests - when and what
* After second day of fever - Check Full Blood Count
* If the test results indicate a drop of white blood cells and
platelet count( eg.4000 WBC / 150,000 PLT) see doctor and repeat FBC
* If the platelet count is below 100,000 - see doctor immediately -
patient needs hospital admission
* The special Dengue test in hospitals can not be deemed accurate, if
the patient has had a mild dengue attack recently he may carry
antibodies in the blood stream so the test will show a 'positive'
reading. Since antibody development will take time, sometimes Dengue
antibody tests specially the rapid tests will be negative.
Indications
Headache or severe headache
Loss of appetite
Pain behind the eye ball
Red colour rash on skin
Slight nasal or gum bleeding
Red colour stools and urine
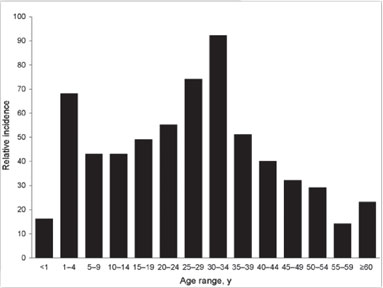 * Some of these symptoms are synonymous with viral flue conditions as
well * Some of these symptoms are synonymous with viral flue conditions as
well
Water
Dengue patients should get,
* A reasonable amount of fluids (electrolyte solutions) like fruit
juices, king coconut, and jeevani. Water alone is not sufficient.
* Rest during the first few days of illness is a critical factor. A
child or any person with suspected Dengue Fever should be allowed to
rest at home.
* Patients should not be given too much fluid after day 2 of illness
because excessive fluids (even oral) can lead to fluid overload in
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF).
* Spread of Dengue from a person to person (via mosquitoes) occurs
when the patient develops fever. So the patient should be under a
mosquito net when he is having fever.
* Physical exertion was closely associated with reported deaths in
dengue patients.(On an analysis of 64 patients who died in 2009 in the
Gampaha district, a majority has had excessive physical exertion within
the first two three days of illness.)
Breeding grounds
In most cases the Dengue breeding ground is in your home itself. If
not, it could be in your immediate neighbour's. The doctors say so
because the Dengue mosquito cannot fly long distances. Therefore if your
child contracts Dengue there is a definite possibility that there is a
breeding ground within your house or surroundings. Start cleaning up!
Papaw juice remedy
No hard evidence has been found to prove that papaw juice boosts
yourplatelet count.
It is not a chance you can afford to take when dealing with a fatal
disease like Dengue.
(This article was prepared with the assistance of Dr. Lalkumar
Fernando and his special medical team at Gampaha Hospital. Dr. Fernando
uses a new and proven highly effective technique in treating Dengue
patients after a special training in Thailand under a Health Ministry
sponsored program).
Molecule that spurs cell's recycling centre may help Alzheimer's
patients
Cells, which employ a process called autophagy to clean up and reuse
protein debris leftover from biological processes, were the original
recyclers. A team of scientists from Paul Greengard's Rockefeller
University laboratory have linked a molecule that stimulates autophagy
with the reduction of one of Alzheimer's disease's major hallmarks,
amyloid peptide. Their finding suggests a mechanism that could be used
to eliminate built-up proteins in diseases such as Alzheimer's, Down
syndrome, Huntington's and Parkinson's.
 |
|
Researchers found that SMER28 was the
most effective compound, and focused their studies on it |
The molecule, called SMER28, spurs autophagy, which in turn
eliminates unwanted materials such as amyloid-beta, the protein
aggregates that cause Alzheimer's plaques. Increasing autophagy, either
through a drug or a natural process such as diet, could improve the
outcome for people with neurodegenerative diseases, the researchers
report in the FASEB Journal.
"Much effort has been carried out to prevent the formation of
amyloid-beta without much success," says Greengard, who is Vincent Astor
Professor and head of the Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular
Neuroscience. "In order to develop better-suited therapies, alternative
approaches are clearly needed. One approach would be the identification
of potential therapeutic targets that enhance the removal of
amyloid-beta, for example, by increasing autophagy."
Most prior strategies to develop Alzheimer's disease drugs were
designed to inhibit the formation of the toxic amyloid-beta.
Greengard, who directs the Fisher Center for Research on Alzheimer's
Disease at Rockefeller, and his colleagues propose a radically different
approach: boosting a cellular mechanism to enhance their clearance. This
approach, says Marc Flajolet, a research assistant professor in
Greengard's lab, may also be beneficial for targeting a hallmark of
advanced Alzheimer's disease, twisted fibers of tau protein that build
up inside nerve cells and cause tangles.
The researchers, led by Yuan Tian, a postdoctoral fellow in
Greengard's lab, tested various compounds for their ability to reduce
the build up of amyloid-beta by exposing cultured cells to compounds
known to activate autophagy. They then compared the effect of these
compounds by removing growth factors from the culture medium, a
well-established stimulant of autophagy known as "starvation."
The researchers found that SMER28 was the most effective compound,
and focused their studies on it to characterize the cellular components
involved in this phenomenon.
They compared the effect of SMER28 on amyloid-beta formation using
normal cells or cells where the expression of genes known to be involved
in autophagy was reduced or abolished. They found that three important
autophagic players were involved, and one of them was essential for
SMER28's effect.
Identifying a cure for Alzheimer's disease remains a major challenge.
Four drugs are currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration
to treat Alzheimer patients. Unfortunately none of these drugs halt
progression of the disease and their impact on cognitive defects are
minimal. On top of that, current strategies are associated with severe
side effects.
This limitation Four drugs are currently approved by the Food and
Drug Administration to treat Alzheimer patients. Unfortunately none of
these drugs halt progression of the disease and their impact on
cognitive defects are minimal. On top of that, current strategies are
associated with severe side effects. was highlighted recently by
failures in various clinical trials.
"Our work demonstrates that small molecules can be developed as
therapies, by activating a cellular function called autophagy, to
prevent Alzheimer's disease," says Flajolet. "By increasing our
understanding of autophagy, it might be possible to stimulate it,
pharmacologically or naturally, to improve the quality of life for aging
people." The results also suggest the power of diet to prevent damage to
neurons.
It has been known that a low calorie diet is beneficial for longer
life expectancy as well as for neurodegenerative diseases such as
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease."Our results suggest that a
low calorie diet might lead to a higher autophagy activity that might
delay or prevent aging and neurodegenerative diseases," says
Flajolet.Source: Rockefeller University
Diabetic retinopathy
by Nilma DOLE
Diabetic retinopathy which is damage to the retina, is caused by
complications of diabetes mellitus, which can eventually lead to
blindness.
"Those who have uncontrolled diabetes and do not get their eyes
checked are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy leading to loss
of sight," said Dr. Irugalbandara of the Colombo General Eye Hospital
and also of the College of Ophthalmologists.
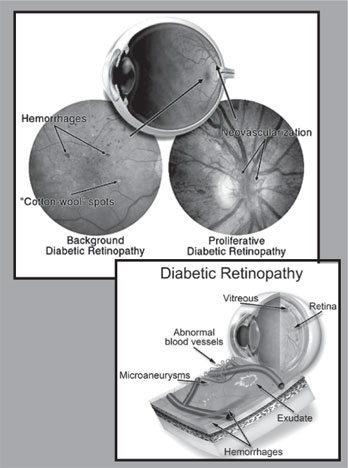 It is an eye problem that affects nearly 80 percent of diabetic
patients who have had diabetes for a long time. However, with proper
treatment and round-the-clock observation, a majority of these cases can
be reduced. It is an eye problem that affects nearly 80 percent of diabetic
patients who have had diabetes for a long time. However, with proper
treatment and round-the-clock observation, a majority of these cases can
be reduced.
Traditionally, capillaries in the optic nerves get damaged or blocked
as a result of uncontrolled diabetes that causes vision loss.
"Diabetics can also develop cataract and glaucoma if not detected and
treated properly," said the doctor. As diabetes affects the circulatory
system of the retina, the first stage is background diabetic
retinopathy.
The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye and a
healthy retina is necessary for good vision.
Circulation problem
The next stage is known as pro-liferative diabetic retinopathy where
circulation problems cause areas of the retina to become
oxygen-deprived. As new, fragile, vessels develop in order to maintain
adequate oxygen levels within the retina, this causes
neo-vascularisation. Unfortunately, these delicate vessels haemorrhage
easily and blood may leak into the retina and vitreous, causing spots or
floaters, along with decreased vision.
In the latter phases of the disease, continued abnormal vessel growth
and scar tissue may cause serious problems such as retinal detachment
and glaucoma. "All people with diabetes, type one and type two, are at
risk and they should go for a routine eye checkup with an
ophthalmologist at least every six months to one year depending on your
control of your diabetes" said Dr. Irugalbandara.
The longer someone has diabetes, the more likely they can get
diabetic retinopathy. During pregnancy, diabetic retinopathy can be
triggered in women with diabetes.
To protect vision, every pregnant woman with diabetes should have a
comprehensive dilated eye exam as soon as possible.
"Often there are no symptoms in the early stages of the disease, nor
is there any pain but don't wait, make sure you check your eyes even if
you don't see a change because it will develop later," said the doctor.
Blurred vision may occur when the macula, the part of the retina that
provides sharp central vision, swells from leaking fluid.
Detection methods
"If new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina, they can
bleed into the eye and block vision," said the doctor. Detection methods
pertaining to diabetic retinopathy tends to vary from one individual to
another.
In general, however, a person tends to have blurred vision, making it
hard to do daily routines such as reading.
Depending on the case, the vision will get better or worse as time
passes.
She further added, "An ophthalmologist checks your retina for early
signs of the disease which includes leaking blood vessels, retinal
swelling, pale, fatty deposits on the retina which show signs of leaking
blood vessels, damaged nerve tissue and any other changes to the blood
vessels."
Diabetic retinopathy is detected during an eye examination that
includes a visual acuity test, pupil dilation, ophthalmoscopy, Optical
Coherence Tomography (OCT), Digital Retinal Screening Programs and Slit
Lamp Biomicroscopy Retinal Screening Programs.
During the first three stages of diabetic retinopathy, no treatment
is needed, unless you have macular oedema (fluid and protein deposits in
the eye's mascular).
"To prevent diabetic retinopathy, people with diabetes should control
their levels of blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol
otherwise it will trigger the condition," said the doctor.Proliferative
retinopathy is treated with laser surgery.
At the beginning, you may notice some loss of your field of vision
but the scatter laser treatment can save the rest of your sight. Scatter
laser treatment works better before the fragile, new blood vessels have
started to bleed.
That is why it is important to have regular, comprehensive dilated
eye exams. Even if bleeding has started, scatter laser treatment may
still be possible, depending on the amount of bleeding. If the bleeding
is severe, you may need a surgical procedure called a vitrectomy where
blood is removed from the centre of your eye.
"Have a balanced diet and control your diseases to an optimum to
prevent diabetic retinopathy. Make sure you get plenty of exercise and
go for regular eye checkups to an ophthalmologist instead of other
experts because your eyes need to be checked with an ophthalmoscope,"
said Dr. Irugalbandara.
|

