Instances of light refraction
 In
our last The world of Science page, we told you what refraction is.
Today, we bring you more facts about refraction. In
our last The world of Science page, we told you what refraction is.
Today, we bring you more facts about refraction.
Did you know that due to atmospheric refraction, there would be an
apparent shift in the position of the Sun during sunrise and sunset?
During sunset, the Sun can be seen for several minutes after it has sunk
below the horizon. Do you know how this happens?
The Earth's atmosphere is dense (thick) near the surface and becomes
rarer higher up. Light travels faster in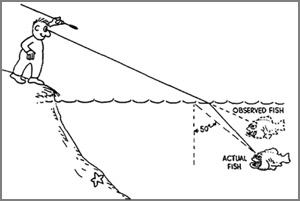 thin air than it does in dense air. The sunrays are coming from rarer to
denser medium. Therefore, the rays bend towards the normal (as shown
last week).
thin air than it does in dense air. The sunrays are coming from rarer to
denser medium. Therefore, the rays bend towards the normal (as shown
last week).
Light from the Sun, which is travelling for longer in thin air than
in dense air, can get to us more quickly, even though the path of these
rays is longer. These rays go through the atmosphere at a steeper slope.
Therefore, for the observer, the Sun appears to be higher in the sky.
The time difference between an actual sunset and the visible sunset
is about two minutes. The Earth's atmosphere is denser near the surface
and rarer above it, and hence, the light path bends gradually to produce
a curved path. This path of least time provides us with a slightly
longer period of daylight each day.
A traveller in the desert thinks there is an oasis or water due to
the apparent shimmering(glistening) reflection he/she sees. The
refraction of light is responsible for many illusions; one of them is
the apparent bending of a spoon partly immersed in water. The sunken
part seems closer to the surface than it really is.
The optical(visual) characteristic of a material is given by what is
called its refractive index (‘). It is defined as
‘ = Speed of light in air or vacuum
(c)/Speed of light in the medium (v)
 When
you see a fish in the water, the fish appears nearer to the When
you see a fish in the water, the fish appears nearer to the surface and closer than it really is. This is due to the refraction of
light, which takes place when light rays pass from the water into the
air.
surface and closer than it really is. This is due to the refraction of
light, which takes place when light rays pass from the water into the
air.
The rays of light coming from the fish are travelling in water before
coming out into the air. While coming out into the air, the rays refract
and bend away from the normal and refracted rays, when produced
backwards, meet at a position, which is slightly above the position of
the fish.
In fact, the refracted rays, which enter the eye, appear to be coming
from this slightly higher position. Hence, the fish appears to be nearer
the surface than it actually is. It is also due to refraction of light
that a thick glass slab appears to be less thick (when seen from above).
Similarly, an ink mark or a line drawn on a piece of paper appears to
be raised and much nearer than it actually is, when viewed through a
glass slab placed over it. A coin placed at the bottom of a container
appears to rise as the container is slowly filled with water, due to the
refraction of light.
The incident of refraction, or bending of light beams, therefore
depends on the optical density of the media and the wavelength of light.
The speed of light is c in a vacuum, but in optical media, it is seen
that the speed of the violet-coloured wavelength is less than that for
the red-coloured wavelength.
Summary
* Light bends towards the normal when the ray goes from a rarer
medium to a denser medium, such as when light goes from air to glass.
* Light bends away from the normal when the ray goes from a denser
medium to a rarer medium, such as when light goes from glass to air.
* Total internal reflection occurs beyond a certain critical angle of
incidence when light goes from a denser to rarer medium.
* If light is along the normal, the refracted wave travels into the
medium along the normal itself.
* The optical characteristic of a medium is defined by its refractive
index.
Compiled by Janani Amarasekara |
