|
SciTech
Better grip for tractor tyres
by Dhaneshi YATAWARA
Having an economy largely based on agriculture, Sri Lanka needs
accelerated developments in the field, particularly in agricultural
engineering. The attention of experts seems to be on the increase at
present. It needs more and not less if we are to be on par with the
global changes.

From primitive method to the new hi-tech |
 |
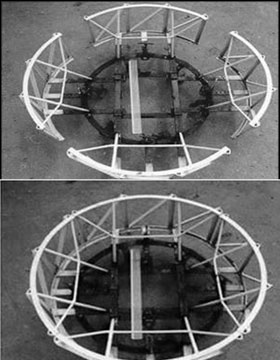 |
| Folding type
mud wheel |

Different types of new mud wheels to suit varying
soil conditions |
| |
Food production needs to be improved and we should reach a level to
be self sufficient as a nation. Sri Lankan agriculture needs a facelift.
Rice being our staple food, increase in its harvest has a greater impact
on the food production. Rice is the staple food of 19 million Sri
Lankans. According to statistics, 1.8 million farmers live on paddy
cultivation. Over 7.3 million hectares are cultivated annually for paddy
production in the country. However, due to low productivity farmers have
not been able to supply the demand for rice in the country.
Adding value to this competitively emerging field the innovation of a
folding type cage wheel for tractors developed by Dr. P.L.A.G. Alwis of
the Faculty of Agriculture, University of Ruhuna can improve the grip of
the regular rubber tyres of small and medium power tractors. Small and
medium tractors became an important factor in paddy cultivation as an
attractive alternative for land preparation using buffalo - the poor
man's tractor. It can be due to the dwindling of the buffalo population
or sociological factors.
This new cage wheel developed under a project funded by the National
Science Foundation, can be considered as an important development for
the farming sector. The use of this cage wheel comes in two folds - it
can improve the use of tractors in wet land paddy field operations and
in road transport.
"A tractor with ordinary high lugged rubber tyres works poorly in
wetlands due to slipping and sinking. To overcome this problem,
different types of gripping aids have been introduced including chains,
tracks and cage wheels," Dr. P.L.A.G. Alwis said explaining his
invention.
According to Dr. Alwis the technicians identify that the working of a
tractor depends on a number of factors - the soil surface on which the
tractor operates being the main factor deciding the efficiency of the
equipment.
But conventional "Mud wheels" for a four wheel tractor have smaller
outer diameter than the tyre to facilitate road transportation.
Therefore when operating in the fields tyres touch the hard pan first
and high slip takes place. Resulting a high travel reduction with
additional time spent on the work including wasting fuel and man power.
This is a considerable economic loss for farmers and tractor owners
and because of this I thought of designing and constructing this new
folding type cage wheels especially with my experience in France during
my PhD studies," the engineering inventor added explaining the pros and
cons of the old machines.
The invented mud wheel consists basically of four foldable folders
and inner mounting system. Each folder has outer cage and three parallel
bars.
Rectangular and angle lugs are fixed to the outer cage of a folder.
The inner mounting system consists of inner ring which is fixed to six
legs and cross bars. Four foldable folders are arranged circularly on
inner mounting system. This gives the capability to have a larger
diameter inthe field operation and smaller on road transportation.
Spring loaded key mechanism has provided to lock the folders at folded
and un-folded position.
The four wheel tractor equipped with the designed cage wheel had 60%
more field capacity and 28% more travelling speed when compared with the
conventional cage wheel. The time taken to plough a hectare of land was
decreased by 40% with the developed new cage wheels. Travelling time was
also reduced by 14%.
The newly developed cage wheel has a quick mounting and dismounting
system. It also gave an improved grip while ploughing fields as the cage
wheel diameter was greater than the type in the expanded position. This
folding type cage wheel can considered as a new aid for small and medium
sized tractors used in both high and wet land conditions. The cage wheel
has simple construction, good serviceability, high field performance in
different soil conditions and low cost.
Rapid prototyping tech quick and cost effective
by Harshini PERERA

Moulds built by the Rapid Prototyping machine |
Technology enables a nation to get into the state of development at
any time. More than any other country, Sri Lanka should take necessary
approaches to reach high in technology. Rapid Prototyping is also one
such measure of technology. The University of Moratuwa has signed a
tripartite agreement with Ministry of Industries and the National
Science Foundation to equip the Engineering Design Centre with a Rapid
Prototyping technology. This is said to be the first machine in Sri
Lanka through which a designer can present his product in complete form
to a potential client or to develop high end products that are required
for specialised industries such as medical and aircraft.
The facility has cost Rs. 40 million for which the Ministry of
Industrial development provided Rs.15 million and the balance Rs.25
million by the National Science Foundation out of the 2008 budget
allocations.
Rapid Prototyping is a technology where the data is fed to the
computer through software known as Computer Aided Design (CAD). Then the
initial three dimensional appearance of the prototype is designed and
fed to the computer in the machine. Inside the machine there lies a VAT,
(a vessel) containing a polymer liquid in which the structure of
prototype is created when the laser beam is placed on it. The structure
is built on a platform on the supportive parts where it is created layer
by layer. Therefore, liquid turns into solids with the application of
light. Later, the supportive parts are extracted using a chemical.
Finally, the prototype is put into UV oven to make it solid.
The service of this technology was available since 19 December 2008.
It was established with the hope of enhancing the design and manufacture
capabilities in electrical and electronic industry. Accordingly, not
only the industry, but many industries which require prototyping
technology such as gem and jewelleries, automobile, ceramic can rely on
it as well.
|

Rapid Prototyping machine |
This prototyping facility addresses the need of designer in supplying
the prototype more quickly and cost effectively. For instance, if a
designer wants to create the prototype built according to his
imagination with metal or wood, it would take two to three months
whereas this machine could do it within a maximum 26 hours. The Director
of Engineering Design Centre, Eng. B.S. Samarasiri explained that this
prototype can be used as the mould as well as the real product. "These
prototypes can also be used as final products as in hearing aids and
medical applications. Because of the high quality they come out which
makes it easy. We have found out that they can produce any prototype
whether it is simple or complicated. This facility was imported from
Germany and an awareness program on this technology was conducted by a
German engineer," he further added.
Eng. Samarasiri explaining further said that, they have already
agreed to render service to Loadstar, Dankotuwa Porcelain, Alankara SKR
(Pvt) Ltd. and LECO for their requests for prototypes." NSF, UOM and MID
has decided to convey a 50% concessional price applicable to all small,
medium and large (Employment above 50 workers) industries for the
servicing of the machines.
We also consider the need of national award winners and one who has
registered with the inventor's commission for the concessional price,"
he stated.
This technology brings sophisticated method to the designers and
inventors deviated from classical methods of making modules. It enables
many with research approaches and profitable approaches to market their
products quickly and reasonably. At the same time since it is based in
an educational institute, the technology can be efficiently transferred
to the students.
South Asia's largest rivers threatened, warns UN
Water resources in three of South Asia's largest river basins are
highly vulnerable, with millions of people at risk of increasing water
scarcity, a new report has found.
|

The River Ganges |
The report - jointly released by the UN Environment Programme and the
Asian Institute of Technology - studied the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM),
Indus and Helmand river basins, all of which span multiple countries
within the region. It lists overexploitation, climate change, and
inadequate distribution and use of water resources among the key threats
to the three basins, calling for "a unique mix of policy interventions
and preferred routes for future water resources development" to tackle
these challenges. Jinhua Zhang, regional coordinator at the UNEP
Division of Early Warning & Assessment told SciDev.Net that countries
should cooperate more to improve how water resources are managed -
particularly to control pollution and improve efficiency - to help stop
further damage to these rivers.
The report assigned each river basin a vulnerability index, based on
resources stress, development pressure, ecological health and management
challenges. The GBM basin is most vulnerable, but water resource systems
in the Helmand and Indus basins are also highly vulnerable.
Extreme population growth in the basins over the last century has put
pressure on the region's water resources, while around two-thirds of the
Himalayan glaciers that feed the basins are receding. Additionally,
groundwater levels in the GBM and Indus basins are declining at a rate
of two to four metres per year due to intense pumping.
In India alone the amount of water per head has decreased from 4,000
to 1,869 cubic metres in the last twenty years.
Zhang told SciDev.Net that further research is needed to identify the
supply of glacial melt for a given area, the amount of wastewater
generated by industry, and strategies for water treatment.
"The per capita availability of freshwater is declining, and
contaminated water remains the greatest single environmental cause of
human illness and death," he says. Improving our knowledge of the
vulnerability of freshwater resources "is therefore essential so that
policymakers can manage this vital resource for the benefit of their
people, their economies and the environment,'' says Zhang.
The report was released this month and is the first of a series. UNEP
is doing similar assessments in North East Asia and South East Asia.
(Source/SciDev.net)
For high quality 'blacklime'
ITI takes valuable steps:
|

The modified dryer
|

Research Officer Neville Amunugoda
|
Food technology in Sri Lanka is at a dire need of significant
developments strong enough to make a difference. Rich with a wide
variety of fruits, vegetables and world renowned spices grown in optimum
weather conditions, Sri Lanka has a promising future in the most
competitive world food market, along with a technology to level up the
product quality.
Identifying this requirement Industrial Technology Institute of Sri
Lanka, recognised to be a centre of excellence in the area of Food
Technology, has taken number of steps in promoting national food
security and safety.
Black Lime
Following these steps Neville Amunugoda, Research Officer attached to
the Food Technology Unit of the ITI designed and constructed a rack
drier which can convert perishable lime in to a product called `Black
Lime' or dried whole lime. This has a high export potential especially
to the Middle Eastern countries as a spice.
According to the Internet in the world this dried lime is also known
as Loomi, Lumi, Omani and Amani. This is a spice used in Middle Eastern
dishes. According to traditions this black lime is made by boiling fresh
lime in salt water and drying it.
Black limes are usually used in legume, seafood or meat dishes. They
are pierced, peeled or crushed before adding them to the dish. After
cooking they become softer and edible. They can also be powdered and
added to rice dishes.
Powdered black lime is also used as an ingredient in Gulf-style `baharat'(a
spice mixture which is also called `kabsa' or `kebsa'). It is very
popular in the Middle East.
Black limes are strongly flavoured. They taste sour and citrus like a
lime but they lack the sweetness of fresh limes. Because they are
preserved they also have a slightly bitter, fermented flavour.
A promising industry
In Sri Lanka manufacturing black lime for export is a promising field
in the food industry with great potentials in the world food market.
Having a rich harvest of high quality lime, especially in the Dry Zone,
is a highly favourable condition for this industry.
"A large amount of energy is required to dry lime. To make black lime
farmers have to adhere to certain quality levels of the end product and
to that lime can not be sun dried," Neville Amunugoda added.
This high energy is required to generate the heat to dry lime. In
Amunugoda's invention this temperature required drying lime is generated
by combustion of biomass.
As the researcher explained the present practice is to use electrical
dryers to dry lime, which is costly for a medium or a small scale
industry. Hence, biomass combustion can be a better solution since dry
flammable agro waste is widely available in the fields.
The problem of using biomass is its smoke with unburnt carbon
particles. This can lower the quality of the black lime. Addressing this
problem Amunugoda found a solution to bring out a non-smoke dryer. This
equipment can handle 60kg of lime at a time.
FT division
The ITI Food Technology division assists food industries by
developing or adapting existing technology, providing necessary
technical support providing machinery and equipment, providing
assistance with identifying unit operations and establishing processing
lines, and engaging in trouble shooting and other forms of consultancy.
The scope of the unit also extends to the vital area of developing and
promoting the production and distribution of nutritional and
nutritionally enriched food in both rural and urban backgrounds.
The section also conducts research programs in the above areas, with
applied problems being handled by multidisciplinary teams. These results
and research findings provide income-generating opportunities for small
and medium industries and are also transferred to industry partners for
larger commercial operations. The FT Section conducts a range of
training programs to meet various needs of the food industry, including
the supervision of Undergraduate and Postgraduate students from national
and international universities. In doing so, the unit also develops
human resources for the industry at large.
Over the years the Food Technology Section has built up a reputation
of expertise in the fields of cereal and bakery technology, Fruit and
Vegetable Processing and Post Harvest Technology, Fish Processing and
Waste Utilization Technology as well.
DY
|


