Watch out for Inter Monsoon lightning hazards
by K. R. Abhayasingha
Lightning activity over Sri Lanka shows peaks during two
Inter-monsoon seasons, March-April and October-November. But since
thunderstorms develop under any atmospheric conditions that are capable
in developing convective clouds, we should be alert in launching
precautionary steps to reduce lightning hazards during all seasons with
special concern in Inter-monsoon seasons. Normally, in addition to the
development of thunder clouds by convection, Sri Lanka is influenced by
frequent cyclonic weather system during the second Inter-monsoon season
resulting widespread thundershowers.
|
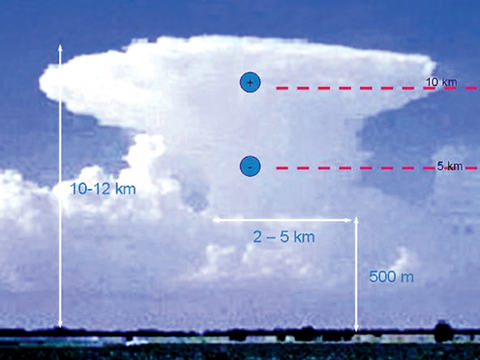
How lightning is reported in Sri Lanka |
Information of lightning incidents in Sri Lanka witnesses for over 50
deaths of human beings and damage to property of billions of rupees
worth every year.
Natural hazard
The electric current of a ground lightning flash (lightning between
the clouds and the earth) is about 25,000 Amperes (25,000 A) on average.
It can vary in the range 2000 - 200000A. The potential difference
between a charged cloud and the earth is about 100 million Volts and the
energy of a lightning flash is about 500 million Joules. Therefore,
lightning is a natural hazard and it causes death and damage outdoors
and indoors as well. Even though being inside a building is the best
precaution against effects of lightning in thunderstorms still it may be
risky if the building is not protected with Lightning Protection
Systems.
During bad weather conditions with thunderstorms, lightning surges
that induces in power and communication supply lines may reach the
inside of a building in a number of ways mainly directly and as side
flashes.
As mentioned earlier, lightning is a natural phenomenon and therefore
it is difficult thing to stop it.
But it has been found that the lightning caused hazards could be
reduced with a number of precautionary measures, which are introduced to
pass the high current surge of a direct or indirect lightning current to
the earth safely. Some of them are,
1) Install good earth for the electric circuit of buildings.
Use Power surge diverters
Supply lines of power and communication can be interrupted by a
gadget called power diverter which is capable in directing high currents
intruding a building along supply cables as a result of a lightning
flash to the ground without allowing it to come into the interior parts
of the building circuit.
3) Installing lightning conductors/arrester.
Direct hit of a lightning flash to a building is the most dangerous
event when the lightning hazards are concerned. Lonely and tall
buildings are the most vulnerable to lightning. Protection of buildings
from direct hits of lightning has been discussed even in the time of the
leading scientist, Benjamin Franklin in this field.
The lightning rod (LR) (or lightning arrester or conductor), which
was first introduced by Franklin, is the widely used device for
protection of buildings even these days. Continuous research in this
field has been useful to apply modifications to the lightning rod to
make it efficient in conducting lightning currents to the ground
protecting the building and the property inside.
The LR usually consists of three parts namely, air terminal, down
conductor and the ground terminal. The installation should be performed
properly, according to the standards, to reach the necessary requirement
of the characteristics of an efficient arrester.
The care has to be taken to have the ground resistance as low as
possible and to avoid margins for sparks of the surge to close by parts
of the building.
There is a very important point to remember. Precautionary steps such
as installing lightning rods and power diverters should be planned and
performed in time without waiting till a lightning flash strikes your
house.
Lightning protection systems are a little costly. But compared with
the cost of the life of a human or cost of electronic infrastructure
installed in present day houses, the protection cost is comparatively
small.
Eventhough our residences, office buildings, school buildings are not
protected against hazards of lightning, the hazards can be mitigated
through practices of precautionary steps in time. Some of them are
briefely mentioned below.
If thunderstorms are forecast, find shelter in a safe place to avoid
exposing yourself to the open air. If the time interval between
lightning flash and hearing thunder becomes less than 15 seconds, move
quickly to a protected location, as there is immediate danger of a
lightning strike nearby.
Different kinds of conducting materials existing in the environment
help in conducting the huge current of a lightning stroke, partly or
fully, from place to place. Electric power supply cables, telephone
cables and TV antenna cables are good examples. Therefore, in
environments with thunderstorms,
(a). Keep electrical instruments disconnected from the main power
supply.
(b). Television antennas should be disconnected from the television
sets and the antenna socket should be placed close to the earth outside
the house.
(c). As far as possible, avoid handling/touching electrical
instruments like refrigerator, electric iron, metal frame, TV, and
radio.
(d). Avoid touching or standing close to tall metal structures, wire
fences and metal clothes lines.
(e). Limit the use of telephones when a thunderstorm is overhead.
Best advice is not to touch the telephone in such instances.
In environments with thunderstorms
(i). Try to avoid loitering in open areas such as paddy fields, tea
estates or play grounds. Specially avoid working in open air holding
metal tools such as mammoty, knife and iron rods. If this cannot be
avoided, crouch, singly, with feet together.
Footwear or a layer of any non-absorbing material, such as plastic
sheet, will offer some protection against ground currents.
(ii). Do not seek shelter under or near isolated tall trees and in
high grounds. If the vicinity of a tree cannot be avoided, seek a
position just beyond the spread of the foliage.
(iii). By sitting down or lying down, reduce the effective height of
the body.
(iv). If in an open boat, keep a low profile. Additional protection
is gained by anchoring under relatively high objects such as jetties and
bridges, provided that no direct contact is made with them.
(v) Avoid riding horses or bicycles, or riding in any open vehicle
such as a tractor.
(vi). Avoid swimming or wading.
Life of a thundercloud is short as 30 minutes. As a result, fatal
lightning occurs during a very short period like 20-20 minutes.
If we are careful to take necessary precautionary steps during that
period it is obvious that the lightning hazards can be reduced. It
should be stressed that the first lightning flash and the flash
following a short break of activity cause most of severe damage to life.
First aid
Lightning hazards are not fatal always. The state of the damage
depends on the path of the lighting discharge through the body and the
intensity of the current. In case of lighting strikes to persons, first
aid should be given to the diseased before taking him for medical
treatment.
Body should be massaged to treat in case of temporary paralysis due
to lightning strikes.
If respiration is disturbed, artificial respiration should be tried.
This could be done by blowing air into the patient's body through his
mouth. In many cases, massage and artificial respiration have to be
given simultaneously.
The writer is Visiting lecturer, Post Graduate Institute of Science (PGIS),
University of Peradeniya, and Retired Director of Meteorology) |

