
Bones come in all shapes and sizes
By now we have learnt many facts about the Human bones. Today, we
bring the third and the last article about bones, on Bodytalk.
You may be already aware as to what bones are. The hard tissue that
forms the skeleton of the body in vertebrate animals is known as a bone.
In the very young, the skeleton is composed largely of cartilage, and is
therefore pliable, reducing the incidence of bone fracture and breakage
in childhood.
The inorganic, or mineral content of bone is mainly calcium,
phosphate and carbonate minerals. The organic content is a gelatinous
material called collagen. As the body grows older, decreases in bone
mass may lead to an increased vulnerability to fractures.
Bone fractures heal naturally, although they are often aided through
restriction of movement in the affected area. Bones assume a variety of
sizes and shapes; however, all bone tissues have a three-layered
composition. A spongy layer forms the interior.
Long bones (such as those in the arms and legs) are hollow, the inner
spaces being filled with marrow (see bone marrow), are important in the
formation of blood cells. Surrounding the spongy, inner layer is a hard,
compact layer that functions as the basic supportive tissue of the body.
The outer layer is a tough membrane called the periosteum, which sheaths
(close fitting covers) most bones.
Although bone appears solid, it contains numerous microscopic canals
permitting the passage of blood vessels and nerve fibres.
Two types of bone are present in most bones: compact, which
constitutes the shaft, and cancellous, an extremely strong variety which
makes up the enlarged ends of the bone.
***
What is the mandible?
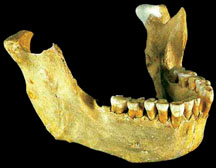
The face has 14 bones;the two that make up the jaw are maxillae
(upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw). The mandible contains sockets
for the teeth, which are embedded in the fibrous tissue. The lower jaw
is the only bony part of the face that moves. Thirty two permanent
teeth, 16 in each jaw, each jaw has four incisors, two canines, four
premolars and six molars.
***
What is known as the funny bone?
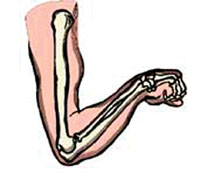
It is a highly sensitive area at the back of the elbow where the
ulnar nerve passes close to the surface of the skin, in a groove between
the end prominence of the humerus (the upper arm bone) and the ulna (the
large forearm bone). A blow to the area causes the nerve to compress
against bone, producing a characteristic tingling in the forearm and the
last two fingers.
***
Where is the occipital bone?
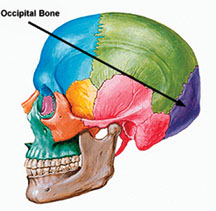
The occipital bone forms the back of the skull. This bone rests on
the spinal column and forms a joint on which the head moves. A system of
muscles and tendons connects the head to the spinal column, the
collaborate and the shoulder blade. These muscles and tendons control
the movement of the head.
Did you know that most of the weight of the head is held in an
upright position by muscles in the neck? Have you noticed that when you
feel sleepy, your head falls forward. The reason behind this is that
when someone becomes sleepy, these muscles relax, resulting in the head
falling forward.
The maxilla, the mandible and the parietal, frontal, sphenoid and
temporal bones are some of the other large bones of the head.
****
Bones in the hand

Bones in the hand are called the matacarpals. The hand consists of
the carpals (wrist bones), the metacarpals (palm bones), and the
phalanges (four fingers and thumb). There are 27 bones in the hand.
The wrist is made up of eight carpal bones, which are arranged in two
rows. Five long metacarpal bones make up the palm. They connect the
wrist with the fingers and thumb.
****
Bones in the foot
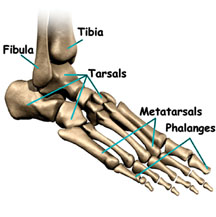
The human foot has 26 bones. They are the 7 tarsals or anklebones,
the five metatarsals or instep bones and the 14 phalanges or the toe
bones.
***
What the smallest bone in our body is
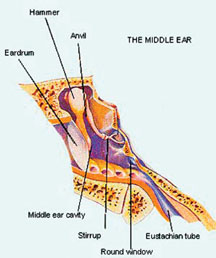
Can you guess what the smallest bone in your body is? Well, it is
called the stirrup and it is in the middle ear. Although it is the
smallest bone, it is part of the system that carries sound signals to
the brain.
The stirrup is only 3mm (1/8 inches) long. Can you believe that it is
about the size of a grain of rice? The footplate of the stirrup bone is
attached to a membrance called the oval window, which leads to the inner
ear. It is connected to two other important small bones called the
hammer and the anvil.
All three of these bones are joined to the eardrum, where sound is
collected before it is sent in the form of nerve signals to the brain. |


