|
observer |
|
|
|
|
|
OTHER LINKS |

|

|

|
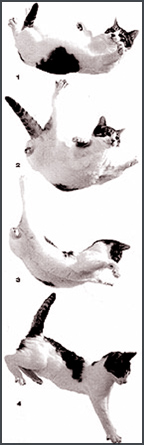
High-Rise SyndromeAs most people know, when a cat is able to see, it will usually land on its feet. It's a neat knack they've had to evolve over eons of climbing trees to cache their kills, evade predators, and look down on the world from a high bough. Although the cat's claws are evolved in an arched shape that is better suited to climbing than for use as weapons, they are still the tools of agile and capable hunters.
Among the feline's numerous predatory gifts is the capacity to fixate on his prey-a skill useful when chasing a shrew through the grass, but a serious disadvantage in the urban world. People living in tall buildings often allow their cats to sit on window ledges and fire escapes, unaware that the traits which allow cats to clamber through trees aren't nearly as effective with metal railings, window panes, and brick. Cats have been known to fixate on something outside and leap or fall from high-rise ledges, an occurrence frequent enough that urban veterinarians have coined a phrase for it: High-Rise Syndrome. Surprisingly, cats falling from lower floors have been found to suffer greater injury than those falling from higher. In fact, when given prompt medical attention, cats which sustain a fall from two to thirty-two stories have a 90% survival rate! According to data from veterinarians in New York, cats are most likely to survive if they fall from a height of six stories, with heights over seven stories being only slightly more dangerous. Clearly, if a person were to take a spill from six stories up the forty-mile-per-hour impact with the Earth would be rather traumatic. The reasons why our feline masters can better deal with such punishment are still somewhat nebulous, but the reigning theory is three fold: It takes a normal cat about a two and a half feet of free-fall to orient himself to feet-down, and it wasn't until the advent of high-speed cameras that the acrobatics were fully understood. Much like an ice skater controls her rate of spin by pulling in or extending her arms, the cat first tucks in his front legs and splays out his rear legs, allowing him to quickly situate his forequarters with the feet down. He then reverses the procedure, extending his front legs and tucking in the rear legs, allowing the hindquarters to rapidly twist into position while the forequarters turn only slightly. Rear legs re-extend when in place, and he's fully deployed. This position is ready for landing, but it also lends the cat a limited aerodynamic-much like the flying squirrel. The ability to increase drag slows a cat's average terminal velocity from a person's 130mph to a much happier 60mph. The fact that cats can twist so quickly to attain feet-down contributes to survivability of High-Rise Syndrome, but it leads into the importance of the third stage. In order to perform the righting manoeuvre, many muscles have to fire in fast and in sequence, and the immediate aftermath of a quick muscle pull is tension; tension is anathema to surviving an impact. The tension is why six to seven stories seems to be the prime falling altitude: it gives the cat time to unwind after the hard twist, and relax into the free-fall for a moment before landing. To record (so far as I can find) the highest a cat has fallen and survived was forty-six stories, but no matter the fall a pet undergoes, one should go look. How rotten would it be to survive a catastrophic trip only to be left abandoned in the world below without access to the food bowl? But just because a cat survives a serious fall doesn't mean he's well. Cats often undergo fractures, broken teeth, or internal injuries upon landing, thus should always be seen by a vet after a fall. The ASPCA notes on their website that sometimes the owners of pets that fall from heights immediately write them off as dead, and don't bother to go and seek out their lost critters. Therein lies a quandary: there is a distinct possibility that the data pertaining to High-Rise Syndrome is tainted. High-Rise Syndrome was added to the lexicon by veterinarians, implying that they gathered the data from animals brought to them for care, but if poor Fluffy ends up a pancake, few cat owners would bother taking him to the vet. Even if the survival rate isn't quite so high as the numbers suggest, it is nonetheless amazing that a significant number of the cats leaping from the upper floors of high-rises live to nap another day. |