|

Elephants or pachyderms,
as they are also known, are the largest living mammals on Earth. We are
familiar with these majestic animals especially because they live in our
country too. Most of you must be aware that there are two species of
elephants, the African elephant and the Asian elephant. Even though both
species belong
 to
the Eliphantidae family there are many physical differences between the
two. One of the most obvious difference is the ears. African elephants
have huge, flappy ears while Asian elephants have smaller ones. We’ll
examine these differences later, but today we introduce you to yet
another member of the elephant family which is in fact believed to be a
subspecies of the Asian elephant - the pygmy elephant of Borneo. It has
gained scientific fame by being recognised as a new subspecies. However,
it is the least understood elephant species in the world. to
the Eliphantidae family there are many physical differences between the
two. One of the most obvious difference is the ears. African elephants
have huge, flappy ears while Asian elephants have smaller ones. We’ll
examine these differences later, but today we introduce you to yet
another member of the elephant family which is in fact believed to be a
subspecies of the Asian elephant - the pygmy elephant of Borneo. It has
gained scientific fame by being recognised as a new subspecies. However,
it is the least understood elephant species in the world.
Now, let’s see why the Borneo species of elephants are special. Just
as much as Asian elephants are different from African elephants, the Borneo pygmy elephants are also very different from their
cousins. With oversized ears, plumb bellies rather straight tusks and
long tails which sometimes drag on the ground, these elephants which are
smaller in size too are said to be cute in appearance. Perhaps they
resemble the much loved cartoon character Dumboo, the elephant. What’s
more, these elephants are found to be unusually tame.
elephants, the Borneo pygmy elephants are also very different from their
cousins. With oversized ears, plumb bellies rather straight tusks and
long tails which sometimes drag on the ground, these elephants which are
smaller in size too are said to be cute in appearance. Perhaps they
resemble the much loved cartoon character Dumboo, the elephant. What’s
more, these elephants are found to be unusually tame.
How come these baby faced pachyderms are so tame compared to their
wild cousins? We need to look into their origin to find probable
answers. There’s much controversy about the origin of this distinct
subspecies among scientists. Scientists claimed that this particular
subspecies is either indigenous (natural to the country) or are the
descendants of a domesticated species of elephants introduced to the
island as a gift exchange between Asian rulers in the 16-18th centuries.
So, one school of thought was that the ancestors of these elephants
separated from the mainland, and the other school of thought was that
they were the descendants of Javan elephants which were being sent as
gifts by the Sultan of Sulu in the 17th century, and were eventually
abandoned in the island.
Finally, recent studies (in 2003) where DNA and dung analysis were
done revealed that these pygmy elephants were a distinct subspecies of
the Asian elephants which ended up being isolated from the mainland
about 300,000 years ago. This discovery made it all the more important
to conserve and protect them from becoming extinct.Presently, the World
Wildlife Fund (WWF) claims, they are threatened with extinction and has
listed them among the 10 most endangered animals in the world. It is
believed that there are not more than 1,000 pygmy elephants left in
Sabah. This follows a two year study carried out in August 2007.A dwarf
among its giant cousins, the highly endangered Borneo pygmy elephant (Elephas
maximus borneensis) is one metre (three feet) shorter than the Asian
elephant. Today these gentle, baby-faced elephants are found only in the
north-eastern part of Boreneo Island, in the Malaysian state of Sabah
(east) and extreme north of Kalimantan. It is found in the tropical
rainforest generally, but as a result a habitat loss they are found
roaming in jungles in flat lowlands and in river valleys; over 40 per
cent of forest cover in Malaysia’s Sabah state, where they are mostly
found today, has been lost to logging, plantation and human settlement
over the last 40 years alone.It has been found that as a result of
habitat loss the animals now forage five times more than they used to. A
herd of about 45 elephants that normally moved up to two kilometres a
day now move up to 6.4 kilometres in one day. They can ingest upto 150
kilograms (330 pounds) of vegetation daily.
It is an alarming fact that these cute lovable animals, the real-life
‘Dumbos’ with their strong resemblance to the cartoon character, should
one day end up like the mammoths which became extinct in the ice-age.
Let’s hope that conservationists will take all the necessary measures to
ensure their numbers grow from just a thousand to many more thousands in
the years to come.
**********
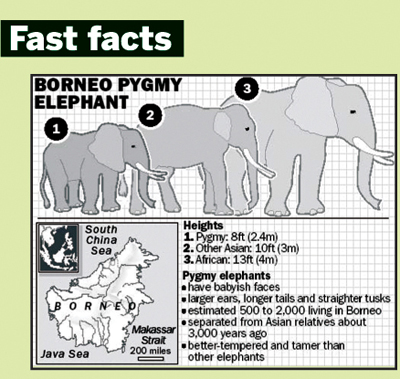
* The Borneo elephant is smaller than all the other subspecies of the
Asian elephant.
* Pygmy elephants are cryptids reported to be living in both Africa
and Asia.
The African Pygmy Elephant (Loxodonta pumilio) is believed to be a
tiny morph of the African forest elephants.
* The term Pygmy elephant should not be confused with dwarf elephant
which is used for a number of extinct species of elephants that evolved
their size due to island dwarfing.
* Elephants are huge, thick-skinned herbivores. They consume plants
including grasses, fruits, vegetables, leaves and barks which they
gathers with their long trunks.
* Male elephants known as bull elephants mature at 10-14 years and
females known as cows at 8-9 years. Their lifespan is 60-70 years.
* Of the two species of elephants, the African and Asian, the latter
(Asian) is more endangered. According to current records, there are only
about 35,000 of them in the wild, spread over 10 countries.
* Expanding human development is one of the main reasons for the
dwindling numbers of elephants, especially the Asian elephants. Such
development disturbs their migration routes, depletes their food sources
and destroys their habitat.
* Borneo’s pygmy elephants are found in the north-east corner of
Borneo (hence the name), a South-east island which is shared by
Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei (refer a map).
* There are claims by Kani tribals dwelling in the rainforests of
India that there are pygmy elephants in the Peppara forest range. They
refer to them as ‘Kallana’. However, the existence of a pygmy variety in
India has not been scientifically ascertained.
* The pygmy elephant is not included in the World Conservation
Union’s Red List of Threatened Species which classifies about 40,000
species according to their risk of extinction.
* In 1996 the Asian elephant was declared endangered.
* The large thorny durian fruit is a delicacy for Borneo pygmy
elephants. They often roll the entire fruit in mud so that they can
swallow it whole, with spikes and all.
* An elephants trunk is actually a long nose used for smelling,
breathing, trumpeting, drinking and also for grabbing things.
* The trunk contains about 100,000 different muscles.
**********
  *
The African elephant is the largest land animal on Earth. It is slightly
bigger than its cousin. *
The African elephant is the largest land animal on Earth. It is slightly
bigger than its cousin.
* Asian elephants have large, but more rounded ears than African
elephants. The African elephants’ fan-like ears are huge. These large
ears radiate heat to keep the animals cool in the African climate which
is too much to bear even for them, sometimes.
* African elephants have two finger-like features on the end of their
long trunk while Asian elephants have only one.
* African elephants are not easily domesticated. |

