|

Ultrasound is not harmful
by Nilma DOLE
“There are various controversies surrounding ultrasounds but they are
not harmful to people and are very important in determining successful
pregnancies,” said consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist,National
Hospital Dr. Viyabhushana. “Ultrasound is a type of sound pressure
associated with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human
hearing which is roughly 20,000 hertz,” he said. According to the
doctor, humans can’t hear the ultrasound waves but animals can hear
them, and this kind of practice is present even in radio waves.
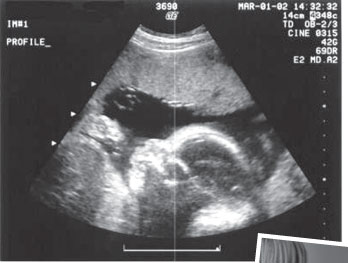 Medical sonography (ultrasonography) is when ultrasound is used to
create images to see a graphic representation of visuals within the
body. “When a pregnant woman comes to do an ultrasound, it is important
to highlight that it is 100 percent safe and it won’t affect the
developing foetus. Plus it can also give some idea about how the baby is
developing in the womb,” said Dr. Viyabhushana. Ultrasounds are
essential and the waves travel from 3 to about 8 megahertz in the body
of a woman who is being checked. “Ultrasound waves cut into the skin but
isn’t detected through the bone. We apply a gel for the ultrasound to be
trapped because it travels faster through air,” said the doctor.
Moreover, ultrasounds are not harmful because they are not rays, or
harmful radioactive waves sent into the body. Soft tissue imaging of
many other parts of the body is conducted with ultrasound. Medical sonography (ultrasonography) is when ultrasound is used to
create images to see a graphic representation of visuals within the
body. “When a pregnant woman comes to do an ultrasound, it is important
to highlight that it is 100 percent safe and it won’t affect the
developing foetus. Plus it can also give some idea about how the baby is
developing in the womb,” said Dr. Viyabhushana. Ultrasounds are
essential and the waves travel from 3 to about 8 megahertz in the body
of a woman who is being checked. “Ultrasound waves cut into the skin but
isn’t detected through the bone. We apply a gel for the ultrasound to be
trapped because it travels faster through air,” said the doctor.
Moreover, ultrasounds are not harmful because they are not rays, or
harmful radioactive waves sent into the body. Soft tissue imaging of
many other parts of the body is conducted with ultrasound.
Dr. Viyabhushana said, “In the first trimester of pregnancy (4 to 8
weeks), an ultrasound is done to see if the pregnancy is ectopic (foetus
developing in the Fallopian tube) or intrauterine (inside the uterus).”
According to the doctor, an ectopic pregnancy is dangerous and should be
carefully detect to prevent complications. “There is also a threat of
bleeding which can be harmful to the foetus and other complications
which can arise if an ultrasound isn’t done to find the cause of the
problem,” said Dr. Viyabhushana.
An ultrasound in 12 weeks determines the foundations of pregnancy
whereby a foetus can be visibly seen. “We can see if the foetus could be
forming as twins, and there are five types of twins which is known to
medical science,” said Dr. Viyabhushana. In addition to this, he said
that the Crown-rump Length can be measured. “This is the measurement of
the length of a human embryo or a foetus from the top of the head
(crown) to the bottom of the buttocks (rump),” he said. The doctor said
that calculating the date of delivery from the exact time of when the
menstruation cycle stops is an unlikely chance. “About 10 to 40 percent
of the time, this theory can’t be applied to women due to various
factors. So we have various data published in medical journals on
test-tube babies (IVF babies) that has information recording the exact
date of pregnancies,”said the doctor. He said that from the Crown-rump
Length, we can determine when the delivery will take place due to
different charts mapping how the foetus is formed and how to calculate
the date. This is known as ‘Date the pregnancy’ or the gestational age,
said the doctor.
 Sex determination is only accurate after 12 weeks and sometimes, this
has to be carefully determined in order to prevent any problems.
“Unexplained foetal deaths, abnormalities, still birth problems all can
be determined in about week 14 of the pregnancy,” said Dr. Viyabhushana. Sex determination is only accurate after 12 weeks and sometimes, this
has to be carefully determined in order to prevent any problems.
“Unexplained foetal deaths, abnormalities, still birth problems all can
be determined in about week 14 of the pregnancy,” said Dr. Viyabhushana.
The two types of ultrasounds are tri-vaginal and tri-abdominal where
tri-vaginal checks vaginal screening and tri-abdominal screens stomach
and tummy problems.
“If there are complications in the stomach wall, certain deformities,
it all can be checked. In fact, we have come across cases where the
foetus have a missing skull, few more fingers and even missing organs,”
said Dr. Viyabhushana.
Anencephaly is rather common problem when a neural tube defect
happens when the cephalic (head) end of the neural tube fails to close,
usually between the 23rd and 26th day of pregnancy, prominently shown as
a missing skull exposing the brain. “Most do not survive birth,
accounting for more than 50 percent of miscarriages. If the infant is
not stillborn, then he or she will usually die within a few hours or
days after birth from cardiorespiratory arrest,” said the doctor.
Even though we think that sometimes ultrasounds may be identified in
the future as harmful risks or even due to fear, currently most doctors
feel that based on available information the benefits to patients
outweigh the risks.
Chikungunya! Once bitten...
by Dr Seemanthini Desai
After the floods, diseases spread by mosquito bites -like chikungunya
- are on the rise. Chikungunya fever is a debilitating viral illness
that is caused by an insect-borne virus, Chikungunya virus (CHIKV).
 The term ‘chikungunya’ means ‘that which bends up’ in the Kimakonde
language (an African language). This refers to the stooped posture of
patients who are afflicted with severe joint pain in this disease. The term ‘chikungunya’ means ‘that which bends up’ in the Kimakonde
language (an African language). This refers to the stooped posture of
patients who are afflicted with severe joint pain in this disease.
Day-time bite
Chikungunya virus is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito.
Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person infected with
chikungunya virus. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to
other humans when they bite them. Aedes aegypti (the dengue fever
mosquito), a household container breeder and aggressive daytime biter,
which is attracted to humans, is the primary carrier of chikungunya
virus to humans.
Known history
Chikungunya fever was first recognized in epidemic form in East
Africa in 1952-1953.
The virus was first isolated in Tanzania. In India CHIKV was first
isolated in Kolkata in 1963.
Following that, epidemics occurred in Tamil Nadu (1964), Maharashtra
(1973), Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka (2005). As of April 29, 2009, the
Directorate of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme in India
has reported over 2,700 suspected cases of chikungunya fever, with no
deaths reported.
The most affected areas in India are the Karnataka, followed by AP,
Goa, and Kerala.
Symptoms
The incubation period (time from infection to illness) can be 2 to 12
days, but is usually three to seven days. Chikungunya virus infection
can cause a debilitating illness. Fever and severe joint pain are
accompanied by chills and constitutional symptoms like headache, extreme
sensitivity (excessive sensitivity to light), conjunctival infection,
myalgia (muscular pain), fatigue (weakness), loss of appetite, nausea
and abdominal pain. Migratory polyarthritis mainly affects the small
joints of the hands, wrists, ankles and feet with lesser involvement of
the larger joints. Erythematous rash may appear on day two or three of
the disease and is most intense on the trunk and limbs, and may peel off
as scales. Red spots under the skin (petechiae) are occasionally seen,
but unlike dengue, this virus is not a regular cause of the hemorrhagic
fever syndrome.
A few patients may develop leucopenia (low white cell counts), mildly
decreased platelet counts, elevated liver enzymes and C-reactive
protein.
Acute chikungunya fever typically lasts for a few days to a few
weeks, but as with dengue fever, some patients have prolonged fatigue
lasting several weeks. Additionally, some people continue to experience
incapacitating joint pain and recurrent joint effusions for several
months to years.
Very rarely the disease becomes fatal by producing complications such
as meningitis and encephalitis (infection spreading to the brain).
Pregnancy and Chikungunya
Pregnant women can become infected with chikungunya virus during all
stages of pregnancy and have symptoms similar to other individuals. Most
infections occurring during pregnancy will not result in the virus being
transmitted to the foetus. The highest risk for infection of the foetus/
child occurs when a woman has virus in her blood at the time of
delivery. There are also rare reports of first trimester abortions
occurring after chikungunya infection. Currently, there is no evidence
that the virus is transmitted through breast milk.
Diagnosis
Chikungunya is diagnosed by ELISA blood test (same as that for HIV
AIDS screening). Blood test is the only reliable way to identify
chikungunya since the symptoms are similar to much more deadly dengue
fever. Also co-occurrence of these diseases is seen in many places.
Treatment
There is no specific antiviral treatment currently
available.Treatment is symptomatic and can include rest, fluids, and
medicines to relieve symptoms of fever and pain. Aspirin should be
avoided during the acute stages of the illness.
In arthritis not responding to analgesics, Chloroquine is
recommended. Infection appears to confer life long immunity. The best
way to prevent chikungunya virus infection is to avoid mosquito bites.
There is no vaccine or prophylactic drug currently available.
(The writer is a Consultant Microbiologist)
Courtesy: BPositive
Reducing your risk of depression
by Amy Scholten
It may not always be possible to prevent depression. However, the
following strategies may help reduce your risk of becoming depressed:
* Be aware of your personal risk of depression.
* Have a psychiatric evaluation and psychotherapy, if needed.
* Develop a strong social and spiritual support system.
* Reduce your stress.
* Exercise regularly.
* Get treatment for alcohol and drug abuse.
* Eat healthfully.
* Get the necessary amount of sleep.
Be aware of your personal risk of depression
Be alert to factors that can increase your risk for depression, such
as:
* Family history, * High levels of stress, * Major life changes, such
as: * Death of a relative, * Assault, * Severe marital or relationship
problems, * Psychological factors, such as: * Low self-esteem, *
Perfectionism, * Sensitivity to loss or rejection, * Inadequate social
support, * Previous episodes of depression, * Chronic physical illness,
* Heart attack, * Chronic pain, * Hormonal changes, including postpartum
depression or menopause, * Anxiety, * Medications that can cause
depression, * Alcohol or drug abuse
Have a psychiatric evaluation and psychotherapy, if needed
If you feel overwhelmed by stress or are experiencing symptoms of
depression, see your doctor for a physical exam and mental health
evaluation. You may be referred for further evaluation or counseling, if
appropriate.
Develop a Strong Social and Spiritual Support System A network of
supportive relationships is beneficial for the prevention and treatment
of depression. Supportive relationships serve as a buffer against
stress, which can sometimes trigger depression.
A high level of religious involvement is associated with a reduced
risk of depression. Spiritual faith in the context of organized religion
can have a buffering effect on depression. In a group setting, it can
provide the additional benefit of social support.
Reduce your stress
A variety of relaxation techniques can help you cope with stressors
that may contribute to depression. Examples include meditation, deep
breathing, progressive relaxation, yoga, and biofeedback. These
techniques help you pay attention to tension in your body and release it
with exercises that help quiet your mind and relax your muscles. You can
also reduce stress by getting adequate sleep, rest, and recreation.
Exercise regularly
Regular exercise helps you relieve stress and may help prevent or
reduce depression. Aerobic exercise and yoga have been found to be
particularly beneficial for reducing stress and improving mood. Aerobic
exercise can raise the levels of brain chemicals that affect mood, such
as endorphins, adrenaline, serotonin, and dopamine. Other benefits of
exercise include: weight loss (if necessary), increased muscle tone, and
higher self-esteem. Yoga provides the benefits of stretching and deep
relaxation.
Courtesy: AHealthyMe
Social phobia: Not just shyness
by Laurie B. Rosenblum
We all get butterflies at some point in our lives, but when fear of
social interaction threatens to take over your life, it’s time to seek
help.
 Suzanne, an intelligent woman in her thirties, had been lonely for
much of her life. She’d been stuck in the same secretarial job because
she was afraid of working with people above her job level. She wanted to
meet a man, but was sure she’d say something stupid and be rejected. Her
few good friends couldn’t get her to go to restaurants or even parties
because she was afraid other people might think she was a sloppy eater.
The few times she agreed to go, her heart was pounding and she began to
blush and perspire. When her primary care physician finally referred her
to a psychologist with experience in anxiety disorders, she was relieved
to discover she had a treatable condition with a name social phobia. Suzanne, an intelligent woman in her thirties, had been lonely for
much of her life. She’d been stuck in the same secretarial job because
she was afraid of working with people above her job level. She wanted to
meet a man, but was sure she’d say something stupid and be rejected. Her
few good friends couldn’t get her to go to restaurants or even parties
because she was afraid other people might think she was a sloppy eater.
The few times she agreed to go, her heart was pounding and she began to
blush and perspire. When her primary care physician finally referred her
to a psychologist with experience in anxiety disorders, she was relieved
to discover she had a treatable condition with a name social phobia.
What is social phobia?
Many people get nervous in certain social or business situations.
There is nothing unusual about feeling anxious before making a
presentation, going out on a first date, going to a party where you
don’t know many people, or having dinner with the boss.
What’s different about social phobia, also known as social anxiety
disorder, is that you have an extreme fear of being judged by other
people and acting in ways that might embarrass or humiliate you. You are
also afraid of becoming the centre of attention and worry that everyone
is looking at you. As a result, you go to great lengths to avoid the
social situations you fear. If you find yourself in one of these
situations, such as a party, you experience intense anxiety that is out
of proportion to the event.
Social phobia usually begins in adolescence, although symptoms like
extreme shyness may occur in earlier years. The disorder is chronic,
although stress may cause the intensity to fluctuate.
How does it differ from shyness?
“Social phobia is not just shyness,” says Stefan Hofmann, Ph.D.,
director of the Social Phobia Treatment Program at Boston University.
“It’s a disorder that causes significant interference with people’s
occupational, personal, and social lives, but treatment is available.”
Although social phobia responds readily to treatment, many people
remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, in part because many people who
suffer from social phobia are embarrassed to admit it. In addition, many
clinicians don’t know how to recognize social phobia and provide
appropriate treatment. Because a large number of people with social
phobia also suffer from depression or alcohol or drug problems,
diagnosis and treatment can become more complicated.
What are the two types?
Some people are afraid of a specific situation, often involving
public speaking or performing. This severe stage fright may dampen the
career of a musician, actor, or salesman. Other people have generalized
social phobia, which is a fear of several, if not most, social
situations.
In both types of social phobia, anxiety before, during, and after
events and avoidance of feared situations significantly interfere with
everyday life. However, generalized social phobia usually has more
serious effects because it occurs in a number of different situations.
In both types of social phobia, physical symptoms may occur. They may
include.
* Heart palpitations
* Excessive sweating
* Blushing
* Dry throat and mouth
* Shaky voice
* Trembling
* Nausea
* Shortness of breath
* Dizziness - Courtesy: aHealthyMe |

