Unknown Pharaoh tomb revealed
Archaeologists working at the southern Egyptian site of Abydos have
discovered the tomb of a previously unknown Pharaoh: Woseribre Senebkay
- and the first material proof of a forgotten Abydos Dynasty, Ca.
1650-1600 BC. Working in cooperation with Egypt's Supreme Council of
Antiquities, a team from the Penn Museum, University of Pennsylvania,
discovered king Senebkay's tomb close to a larger royal tomb, recently
identified as belonging to a king Sobekhotep (probably Sobekhotep I, Ca.
1780 BC) of the 13th Dynasty.
|
The newly discovered tomb of pharaoh Senebkay dates to Ca.
1650 BC during Egypt's Second Intermediate Period |
The discovery of pharaoh Senebkay's tomb is the culmination of work
that began during the summer of 2013 when the Penn Museum team, led by
Dr. Josef Wegner, Egyptian Section Associate Curator of the Penn Museum,
discovered a huge 60-ton royal sarcophagus chamber at South Abydos.
The sarcophagus chamber, of red quartzite quarried and transported to
Abydos from Gebel Ahmar (near modern Cairo), could be dated to the late
Middle Kingdom, but its owner remained unidentified.
Mysteriously, the sarcophagus had been extracted from its original
tomb and reused in a later tomb -- but the original royal owner remained
unknown when the summer season ended.
In the last few weeks of excavations, fascinating details of a series
of kings’ tombs and a lost dynasty at Abydos have emerged.
Archaeologists now know that the giant quartzite sarcophagus chamber
derives from a royal tomb built originally for a pharaoh Sobekhotep --
probably Sobekhotep I, the first king of Egypt's 13th Dynasty. Fragments
of that king's funerary stela were found just recently in front of his
huge, badly robbed tomb.
A group of later pharaohs (reigning about a century and a half later
during Egypt's Second Intermediate Period) were reusing elements from
Sobekhotep's tomb for building and equipping their own tombs. One of
these kings (whose name is still unknown) had extracted and reused the
quartzite sarcophagus chamber.
Another king's tomb found just last week is that of the previously
unknown pharaoh: Woseribre-Senebkay.
A lost Pharaoh and a forgotten dynasty
The newly discovered tomb of Pharaoh Senebkay dates to Ca. 1650 BC
during Egypt's Second Intermediate Period.
The identification was made by Dr. Wegner and Kevin Cahail, student,
Department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilisations, University of
Pennsylvania.
The tomb of Senebkay consists of four chambers with a decorated
limestone burial chamber.
The burial chamber is painted with images of the goddesses Nut,
Nephthys, Selket, and Isis flanking the king's canopic shrine.
Other texts name the sons of Horus and record the king's titulary and
identify him as the “king of Upper and Lower Egypt, Woseribre, the son
of Re, Senebkay.”
Senebkay's tomb was badly plundered by ancient tomb robbers who had
ripped apart the king's mummy as well as stripped the pharaoh's tomb
equipment of its gilded surfaces.
Nevertheless, the Penn Museum archaeologists recovered the remains of
king Senebkay amidst debris of his fragmentary coffin, funerary mask,
and canopic chest.
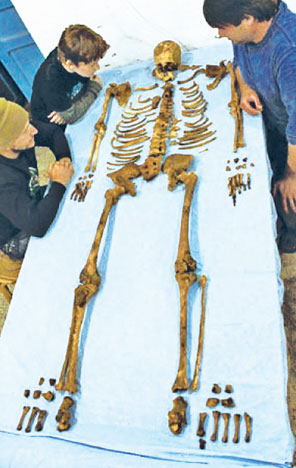
Preliminary work on the king's skeleton of Senebkay by Penn graduate
students Paul Verhelst and Matthew Olson (of the Department of Near
Eastern Languages and Civilizations) indicates he was a man of moderate
height, Ca. 1.75 m (5'10), and died in his mid to late 40s.
The discovery provides significant new evidence on the political and
social history of Egypt's Second Intermediate Period.
The existence of an independent “Abydos Dynasty,” contemporary with
the 15th (Hyksos) and 16th (Theban) Dynasties, was first hypothesized by
Egyptologist K. Ryholt in 1997.
The discovery of Pharaoh Senebkay now proves the existence of this
Abydos dynasty and identifies the location of their royal necropolis at
South Abydos in an area anciently called Anubis-Mountain.
The kings of the Abydos Dynasty placed their burial ground adjacent
to the tombs of earlier Middle Kingdom pharaohs including Senwosret III
(Dynasty 12, Ca. 1880-1840 BC), and Sobekhotep I (Ca. 1780 BC). There is
evidence for about 16 royal tombs spanning the period Ca. 1650-1600 BC.
Senebkay appears to be one of the earliest kings of the Abydos Dynasty.
His name may have appeared in a broken section of the famous Turin
King List (a papyrus document dating to the reign of Ramses II, Ca. 1200
BC) where two kings with the throne name “Woser...re” are recorded at
the head of a group of more than a dozen kings, most of whose names are
entirely lost.
The tomb of Pharaoh Senebkay is modest in scale. An important
discovery was the badly decayed remains of Senebkay's canopic chest.
This chest was made of cedar wood that had been reused from the
nearby tomb of Sobekhotep I and still bore the name of that earlier
king, covered over by gilding.
Such reuse of objects from the nearby Sobekhotep tomb by Senebkay,
like the reused sarcophagus chamber found during the summer, provides
evidence that suggests the limited resources and isolated economic
situation of the Abydos Kingdom which lay in the southern part of Middle
Egypt between the larger kingdoms of Thebes (Dynasties 16-17) and the
Hyksos (Dynasty 15) in northern Egypt.
Unlike these numbered dynasties, the pharaohs of the Abydos Dynasty
were forgotten to history and their royal necropolis unknown until this
discovery of Senebkay's tomb.
“It's exciting to find not just the tomb of one previously unknown
pharaoh, but the necropolis of an entire forgotten dynasty,” noted Dr.
Wegner.
“Continued work in the royal tombs of the Abydos Dynasty promises to
shed new light on the political history and society of an important but
poorly understood era of Ancient Egypt.”
- ScienceDaily
|

