|
observer |
|
|
|
|
|
OTHER LINKS |

|

|

|
|
Be with IT Sonic's DesktopsThe different generations of computers Welcome back to our explorative journey on the evolution of computers. As I introduced in the last edition, this journey started as a result of man's increasing need to perform various computations (calculations). Initially, he used his fingers to perform these calculations. Thereafter, various simple mechanical devices came into being, and they evolved in to electronic logic devices since mechanical devices could not operate at faster speeds. As the field of electronics developed, it resulted in the computer evolving in to its present state. Let's go further into this journey, through the many generations of computers. 1st Generation (1939-1954) This was the point when we said goodbye to fully mechanical computers and started using electronics. The invention of the vacuum tube was a breakthrough made in this era. This device could amplify, switch or modify a signal by controlling the movement of electrons in a vacuum (evacuated) region.
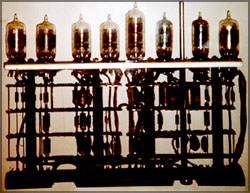
It looks more or less like a bulb, and operates in a similar fashion to a transistor. But the disadvantages of this machine were its size (it was the size of a room), the high power consumption and unpredictable lifetime. The Colossus (1943), ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator - 1954) and UNIVAC (1951) were popular computers during this time. ENIAC was a large contraption which weighed 30 tons, was 30 metres long and had 18,000 vacuum tubes. Imagine that! The UNIVAC was a developed version of the ENIAC which was the first commercial computer and featured a magnetic tape storage system. Magnetic drum memory and punch cards for inputting data were key features in this generation. Machine language or pure binary was used to programme operations. 2nd Generation (1954-1959) The invention of the transistor in 1947 by Schockley, Bardeen and Brattain at Bell Labs was a major
breakthrough for computers in the 1950s. The vacuum tubes were replaced by the low power, reliable and tiny transistors, which considerably reduced the size of computers. Punch card inputs and printouts as output still remained in this generation. But, where programming is concerned, assembly language comprising simple English words that directly mapped on to a machine code came into being. High level languages such as FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslation, 1954) and COBOL (COmmon Business Oriented Language, 1959) also came into existence. This was the generation of computers which started using instructions stored in memory; this was done using magnetic core memory, while moving away from magnetic drum memory. 3rd Generation (1959-1971) More integration! Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments invented and patented the IC (Integrated Circuit) in 1959, and it became a better option than using pure transistors and magnetic core memory. Since an IC consists of many miniature transistors, it dramatically increased the speed and efficiency of computers, resulting in them being scaled down further. Another breakthrough in this era was micro-programming. This is basically using 'control words' or binary expressions stored in memory to activate the relevant circuitry of the computer. Punch cards and printed output became obsolete (non-existent), keyboards and monitors came into being and operating systems were born. In 1964, Control Data Corporation, delivered the first Super Computer, DCD 6600. 4th Generation (1971-present) The significance of this generation is the birth of the micro-processor. This was a result of VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration), which could hold thousands of components on one silicon chip. Gilbert Hyatt at Micro Computer Corporation patented the micro-processor in 1971. Intel made the first commercial micro-processor, I4004. IBM introduced the first eight-inch memory disk known as the 'floppy disk'. In 1973, IBM developed the first true sealed hard disk drive, called the 'Winchester', using two 30 Mb. There is some interesting news for you! In 1977, Nintendo in Japan began making computer games that stored the data on chips inside a game cartridge. The great World Wide Web was developed in 1991. It was in the fourth generation that GUI (Graphical User Interface), mouse and hand-held devices too came in to existence. We are still in this generation with a lot of new stuff coming up each day. 5th Generation (Present and beyond) The fifth generation, which is yet to come, is looking at Artificial Intelligence. The goal of this generation is to develop devices which respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organisation. The use of super conductors and nanotechnology will play a key role in this endeavour. |