
Tides and the Moon
The word tide is not strange to us any more. But have you wondered
what a tide is, and questioned the link between the Moon and the tides?
For those who are not aware of the tides, the word "tides" is a
common term used to define the alternating rise and fall in sea level
with respect to the land. These are produced by the gravitational
attraction of the Moon and the Sun.

To a much smaller extent, tides also occur in large lakes, the
atmosphere, and within the solid crust of the Earth, acted upon by these
same gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun.
Have you heard of lunar tides? Tides are created because the Earth
and the Moon are attracted to each other, just like magnets are
attracted to each other. The Moon tries to pull at anything on the
Earth, to bring them closer. But, the Earth is able to hold on to
everything except the water.
Since the water is always moving, the Earth cannot hold on to it, and
the Moon is able to pull at it. Each day, there are two high tides and
two low tides. The ocean is constantly moving from high tide to low
tide, and then back to high tide. There are about 12 hours and 25
minutes between the two high tides.
Tides are the periodic rise and fall of large bodies of water. Winds
and currents move the surface water, causing waves.
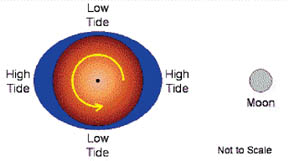
The gravitational attraction of the Moon causes the oceans to bulge
out in the direction of the Moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite
side, since the Earth is also being pulled towards the Moon (and away
from the water on the far side).
Ocean levels fluctuate (change) daily as the Sun, Moon and Earth
interact. As the Moon travels around the Earth and as they, together,
travel around the Sun, the combined gravitational forces cause the
world's oceans to rise and fall. Since the Earth is rotating while this
is happening, two tides occur each day.
What are the different types of tides? When the Sun and Moon are
aligned, there are exceptionally strong gravitational forces, causing
very high and very low tides which are called spring tides, though they
have nothing to do with the season.
When the Sun and Moon are not aligned, the gravitational forces
cancel each other out, and the tides are not as dramatically high and
low. These are called neap tides.
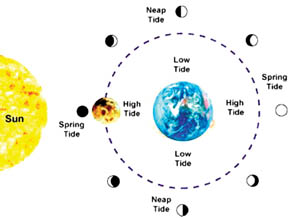
Spring Tides - When the Moon is full or new, the gravitational pull
of the Moon and Sun are combined.
At these times, the high tides are very high and the low tides are
very low. This is known as a spring high tide. Spring tides are
especially strong tides and occur when the Earth, the Sun, and the Moon
are in a line.
The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun both contribute to
the tides.
Neap Tides - During the Moon's quarter phases, the Sun and Moon work
at right angles, causing the bulges to cancel each other.
The result is a smaller difference between high and low tides and is
known as a neap tide. Neap tides are especially weak tides.
They occur when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun are
perpendicular (at a 90 degree angle) to one another (with respect to the
Earth).
The Proxigean Spring Tide is a rare, unusually high tide. This very
high tide occurs when the moon is both unusually close to the Earth at
its closest perigee (point nearest to the Earth in the Moon's orbit),
called the proxigee and in the New Moon phase (when the Moon is between
the Sun and the Earth). The proxigean spring tide occurs at most, once
every one and a half years.
****
Facts about lunar tides
* The gravitational force of the Moon is one ten-millionth that of
the Earth, but when you combine other forces such as the Earth's
centrifugal (moving away from the centre) force created by its spin, you
get tides.
* The Sun's gravitational force on the Earth is only 46 per cent that
of the Moon, making the Moon the single most important factor for the
creation of tides.
* The Sun's gravity also produces tides, but since the forces are
smaller, as compared to those of the Moon, the effects are greatly
decreased.
* Tides are not caused by the direct pull of the Moon's gravity. The
Moon is pulling upwards on the water, while the Earth is pulling
downwards. The slight advantage to the Moon results in tides.
* Whenever the Moon, Earth and Sun are aligned, the gravitational
pull of the Sun adds to that of the Moon, causing maximum tides.
* Spring tides happen when the Sun and Moon are on the same side of
the Earth (New Moon) or when the Sun and Moon are on opposite sides of
the Earth (Full Moon).
* Spring tides and Neap tide levels are about 20 per cent higher or
lower than average.
* Offshore, in the deep ocean, the difference in tides is usually
less than 1.6 feet.
* The surf grows when it approaches a beach, and the tide increases.
In bays and estuaries, this effect is amplified (stronger).
* The highest tides in the world are at the Bay of Fundy in Nova
Scotia, Canada. There, the tides have a range of 44.6 feet.
* Because the Earth rotates on its axis, the Moon completes one orbit
in our sky every 25 hours (not to be confused with the Moon's 27 day
orbit around the Earth), we get two tidal peaks as well as two tidal
troughs (low point between two waves). These events are separated by
about 12 hours.
* Since the Moon moves around the Earth, it is not always in the same
place at the same time each day. So, each day, the times for high and
low tides change by 50 minutes.
* The type of gravitational force that causes tides is know as 'Tractive'
force. |


