 Nanotechnology - path to the future Nanotechnology - path to the future
Nanotechnology is a discipline which has been booming in many areas
useful for humans such as medicine, engineering, computer and IT,
materials, energy generation and consumer goods.
What is nanotechnology?
|

Pic 1 |
In simple terms, nanotechnology can be defined as a field of research
and development involving building structures in nanometre scale (i.e. 1
- 100 nm). Nano is a Greek word for 'dwarf'. This implies that
nanotechnology deals with very small things.
In scientific language, 'Nano' is used to denote 10-9. Hence a
nanometre is one billionth of a metre (1/1,000,000,000).
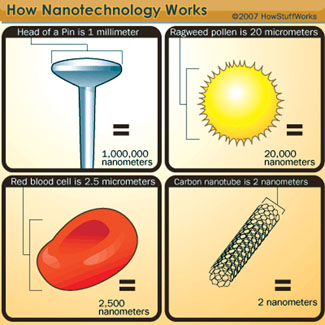
To understand how small a nano particle - which has a diameter of 1-2
nm - is, look at this illustration (Pic 1). If this nano particle is big
as a football, then the football is big as the Earth.
Carbon nano tubes and 'carbon bucky balls' are two important nano
scale structures used in nanotechnology.
* Carbon bucky balls
C60 or carbon bucky ball is a nano scale spherical (round) molecule
made of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a perfect symmetrical structure.
(See pic 2)
The diameter of a single C60 molecule is around 1-2 nm. These were
first discovered in 1985 by three American scientists - Robert Curl,
Harold Kroto and Richard Smalley.
|
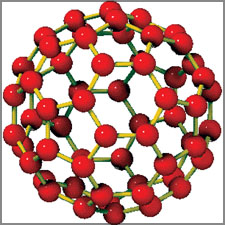
(Pic 2) Carbon bucky balls |
They received the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1996 as this was a
very important and useful discovery. Research is currently carried out
using C60 molecules in research laboratories around the world,
especially on producing fuel cells.
* Carbon nano tubes
The Carbon Nano Tube (CNT) is a tube-like structure generally made of
carbon atoms assembled in hexagons. This was discovered by Sumio Lijima,
a Japanese scientist, in 1991. The diameter of a single nano tube is
around 2-4 nm and can be extremely long. When we compare this with human
hair, it is 80,000 times smaller in diameter.
Nano tubes have extra ordinary physical properties. They are many
times stronger than steel wires, lighter than aluminium, possess high
heat conductivity and have different electrical properties.
Today, more and more CNT applications are moving from the research
labs into commercial products. Now CNT is used for making high strength
and lightweight tennis rackets and bicycles, producing smaller
electronic devices and for various other applications in health care,
aerospace and defence.
Currently, thousands of metric tons of nano tubes are produced
annually, all over the world.
Nanotechnology is used to manipulate (manage) atoms, molecules and
nano-size particles in a precise and well-controlled manner to build new
materials with novel properties.
Current applications
|
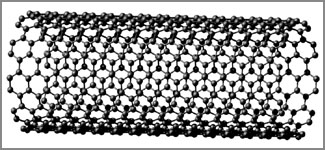
Carbon nano tubes |
Some of the key current and potential short-term applications of nano
materials are given below. Most current applications represent
evolutionary developments of existing technologies: for example, the
reduction in size of electronic devices.
* Sunscreens and cosmetics
Nano-sized titanium dioxide and zinc oxide are currently used in some
sunscreens, as they absorb and reflect ultraviolet (UV) rays and yet are
transparent to visible light and so are more appealing to the consumer.
Nano-sized iron oxide is present in some lipsticks as a pigment, but
it is understood that it is not used by the European cosmetics sector.
However, the use of nano particles in cosmetics has raised a number of
concerns about consumer safety.
* Clays
Clays containing naturally occurring nano particles are widely used
as construction materials and are undergoing continuous improvements.
Clay particle-based composites containing plastics and nano-sized flakes
of clay are also becoming popular in applications such as manufacturing
of car bumpers.
* Coatings and surfaces
Coatings with thickness controlled at the nano or atomic scale have
been in routine production.
 Recently developed applications include the self-cleaning window,
which is coated in highly activated titanium dioxide, engineered to be
highly hydrophobic (water repellent) and antibacterial, and coatings
based on nano particulate oxides that destroy chemical agents. Wear and
scratch-resistant hard coatings are significantly improved by nano scale
intermediate layers (or multilayers). Recently developed applications include the self-cleaning window,
which is coated in highly activated titanium dioxide, engineered to be
highly hydrophobic (water repellent) and antibacterial, and coatings
based on nano particulate oxides that destroy chemical agents. Wear and
scratch-resistant hard coatings are significantly improved by nano scale
intermediate layers (or multilayers).
Textiles
A range of enhanced textiles, such as breathable, waterproof and
stain-resistant fabrics are also being developed with the help of
nanotechnology. The dust and stain may not retain in the fabric as the
pore sizes of these nano materials are smaller than the dust and stain
particles.
Tougher and harder cutting tools
Cutting tools made of nano crystalline materials, such as tungsten
carbide, tantalum carbide and titanium carbide, are more wear and
erosion-resistant, and last longer than their conventional (customary)
large-grained counterparts. They are finding applications in the drills
used to bore holes in circuit boards. These cutting tools are tougher
and harder than the conventional ones.
Paints
Incorporating nano particles in paints could improve their
performance, for example, by making them lighter and giving them
different properties. Thinner paint coatings ('light weighting'), used
for example on aircraft, would reduce their weight and could be
beneficial to the environment.
Nano paints are brighter and durable than conventional paints. Other
novel, and more long-term, application of nano paint is producing paints
which can change colour in response to change in temperature or chemical
environment.
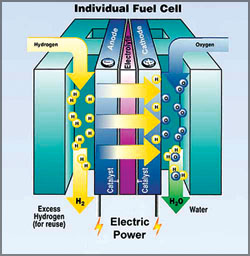
Fuel cells
 One of the suggested solutions for the future fuel crisis is
generating electric energy from fuel cells, especially for vehicles.
Hydrogen is used as the immediate fuel in fuel cells, which can be
generated from hydrocarbons by catalytic (induced) reforming. One of the suggested solutions for the future fuel crisis is
generating electric energy from fuel cells, especially for vehicles.
Hydrogen is used as the immediate fuel in fuel cells, which can be
generated from hydrocarbons by catalytic (induced) reforming.
The potential use of nano-engineered membranes to intensify catalytic
processes could enable higher-efficiency, small-scale fuel cells.
One of the major practical concerns with regard to fuel cells is
storing hydrogen in a portable manner. Research is being conducted to
use nano materials such as fullerenes, as a hydrogen storage media.
Nano technology provides solutions to many problems currently faced
by the people. As an outcome, it is widely becoming popular throughout
the globe. We are certain to see many more applications of
nanotechnology in the near future.
Reference: http://www.nanowerk.com, http://www.nanoforum.org/
Chintaka Nadun Ratnaweera, Scientific Officer, National Scientific
Foundation. |
