Nuclear power as a clean energy
By Indeewara Thilakarathne
[email protected]
Sri Lanka could posses NPS’s in 10-15 years - Dr. W. Abeywickreme,
Chairman Atomic Energy Authority of Sri Lanka :
|

Nuclear power station |
Here in an interview with ‘Sunday Observer’ Dr. W. Abeywickreme,
Chairman Atomic Energy Authority of Sri Lanka explores the possibility
of setting up Nuclear Power Stations (NPS’s) in Sri Lanka as nuclear
power is a clean energy.
Though the initial cost is higher than that of a coal power station,
operational and maintenance cost is very low compared to coal plants and
carbon emission is zero.
He pointed out if Sri Lanka has taken a policy decision now, the
country can posses NPS’s in 8-10 years time with the technical
assistance from IAEA (International Atomic Energy Authority).
“If Sri Lanka has taken a policy decision today, Sri Lanka could
posses NPS’s within 8-10 years.
Though a policy decision has not yet been taken to construct NPS, an
important initiative has been taken to explore the possibility of using
nuclear power for power generation. Minister of Science and Technology
Prof. Tissa Vitharana has taken an interest in this regard.
This is an important initiative considering the fact that nuclear
option has not been included in action plan for the next fifteen years,”
said Dr. W. Abeywickreme, Chairman Atomic Energy Authority of Sri Lanka.
Dr. Abeywickreme was of the view that a policy decision was made with
regard to the establishment of NPS’s in Sri Lanka, technical expertise
can be obtained from IAEA and training of personnel can be done. So far
the biggest hurdle in the setting up of NPS in Sri Lanka is until
recently nuclear option has not been considered as an option.
A complex process
Though nuclear seems to be an immediate option, setting up of NPS is
a complex process which consumes considerable time. The NPP (Nuclear
Power Planning) is to be done. According to Dr. Abeywickreme, at
present, countries like Bangladesh, Indonesia, Thailand, China and
Malaysia have taken steps to implement NPP projects.
In 1980s the IAEA conducted a programme for Nuclear Power Planning
and a decision was taken to train technical staff. The initial step was
to train technical person from the University of Moratuwa in USA up to
the PhD level in Nuclear Power Engineering with a view to introducing
Nuclear Power Planning to the Engineering syllabus of the campus.
IAEA also assisted the University of Peradeniya to initiate a
programme of study in the discipline of Nuclear Neutron-Physics.
However, those initial ground work for setting up of NPS have not
been followed up.
Against the backdrop of rising oil prices and environment concerns,
focus has, once again, turned on to nuclear as a clean energy with zero
carbon emission.
Currently the national grid with about 2000 megawatts and though it
is a sufficient the base-load requirements for a NPS, Electricity Board
opted for coal power plants. In order to run a NPS, it is required that
the country should have a minimum base-load capacity in constant
operation and the available feasible nuclear power plant should match
that base-load.
However the present policy of the Electricity Board is to go for coal
power plants for the base-load management. This has been the strategy
adapted by Electricity Board till 2020.
Compared to Sri Lanka, India is ahead in its nuclear planning and has
already been planned to set up a NPS in Pudenkulam which is close to Sri
Lanka.
Public Acceptance
“As public acceptance and awareness on nuclear power is vital for
future prospects of using nuclear power in Sri Lanka, Atomic Energy
Authority of Sri Lanka has initiated Young Nuclear Scientists’ Forum (YNSF)
with the aim of attracting young generation (members below 37 years)
specially O/L and A/L students and University students. It is an
exercise in raising public awareness on nuclear power.
We will also launch public awareness programme on July 4, 2008 at the
Public Library auditorium on the use of nuclear energy in Sri Lanka
“says Dr. Abeywickreme emphasizing the fact that public awareness on
nuclear energy and acceptance of it as clean energy is vital for wide
use of nuclear power in Sri Lanka for power generation.
Demonizing nuclear power especially after the Chernobyl disaster has
over the years created a negative perception of nuclear power.
However, compared to coal power which incurs considerable cost of
purchasing, storing, transporting and loading and unloading, nuclear
energy is emission free and the technology can be applied in many other
areas such as Nuclear medicine (including X-rays, isotope production,
cancer-treating chemicals and non invasive medical procedures), Food
Irradiation (irradiated food ensure people receiving balance, healthy
and wholesome diet) and Waste Management (safely storing radio-active
waste from hospitals, industries and power stations).
One of the principle advantages of nuclear power is the substantial
contribution it makes in reducing CO2 emission.
Site selection
If a policy decision has been taken to set up a NPS in Sri Lanka, the
primary consideration should be the selection of a site for the plant.
AEA is of the view that an appropriate site would be set up in an island
like Mannar or Delft considering the crucial factors such as wastes
disposal system and public acceptance.
“Another vital factor in setting up a NPS in Sri Lanka is the
availability of uranium or thorium. Once the plant commenced operation,
there will be enough uranium or thorium resources to sustain the
operation in the world,” said Dr. Abeywickreme.
Although thirty percent of world’s thorium resources are concentrated
in South Asian region (Sri Lanka and India), thorium resources have not
been tapped for power generation.
India has planned to use thorium for its second generation of NPS and
the available resources are sufficient in India to propel to industrial
heights. Sri Lanka’s thorium resources are believed to be deposited in
the coastal line from Moratuwa to Kalutara and in the areas like
Kerawala Pitiya and Buththala.
“In fact, we had an initial discussion with the chairman of
Geological and Mine Bureau on the exploration of thorium in Sri Lanka.
At least, if a policy decision is taken at this juncture, we can
accelerate our programme like the one which is looking into the
availability of thorium in Sri Lanka.
It is a long term process that will take 10-15 years” said Dr.
Abeywickreme.
Currently Atomic Energy Authority of Sri Lanka provides host of
services including Non Destructive Testing (NDT) Services, NTD training
services, analytical services and domestic calibration services.
The world at a glance
The present situation in nuclear power generation throughout the
world is extremely varied.
In the 30 countries that have nuclear power generation capacity, the
percentage of electricity coming from nuclear reactors ranges from 78%
in France to just 2% in China.All told, as of March 2008, there are 439
nuclear power plants around the world, while 35 more are under
construction. The USA has the most with 104, France is next with 59,
then Japan with 55 and Russia has 31 and seven more under construction.
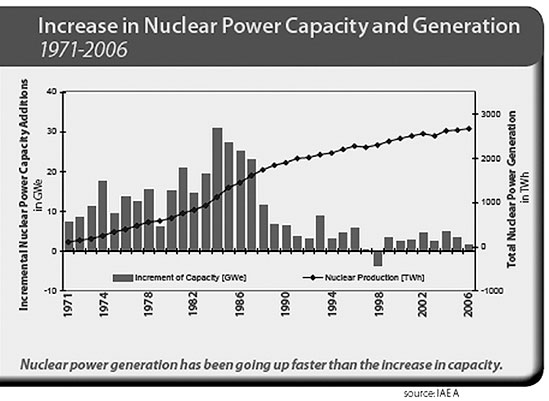 The expansion in nuclear power generation is centered in Asia. A
total of 20 of the 35 plants under construction are in Asia, while 28 of
the last 39 plants connected to the grid are also in Asia. The expansion in nuclear power generation is centered in Asia. A
total of 20 of the 35 plants under construction are in Asia, while 28 of
the last 39 plants connected to the grid are also in Asia.
Asia: Expanding Scene
But what is the outlook for nuclear power generation in individual
countries around the world?
Our overview starts with the countries of Asia, the world’s region
where most of the expansion is taking place.
India
India gets less than 3% of its electricity from nuclear, but it is,
along with China and Russia, one of the leaders in current new
construction, boasting six of the world’s 35 reactors under
construction.
India’s future plans, however, are even more impressive: an
eight-fold increase by 2022 to 10% of the electricity supply and an
overall 70-fold increase to 2052 to 26%. A 70-fold increase figure
certainly sounds remarkable, but it works out to be an average growth
rate of 9.5% per year, which is a bit less than the average global
nuclear growth from 1970 through 2002. So it is hardly unprecedented.
China
China, like India, faces a steep growth in energy demand and is
trying to expand its generating capacity using all possible energy
sources, including nuclear power. China has six reactors under
construction and plans nearly a five-fold expansion by 2020.
However, because the country’s energy demand is growing so fast, that
would still amount to only 4% of electricity generated by then. Looking
ahead, China is a potential supplier of technology and services,
particularly in Asia.
Japan
Moving across the Sea is Japan, a country with 55 reactors, one more
under construction and plans to increase nuclear power’s share of
electricity from 30% in 2006 to over 40% before 2020.
Republic of Korea
Another Asian country with a significant commitment to nuclear
technology is South Korea, which has 20 reactors in operation and three
more under construction. Nuclear power already supplies nearly 40% of
South Korea’s electricity.
(Source IAEA) |
