|

Prevention is the keyword:
Have a balanced diet, exercise regularly
By Thulasi MUTTULINGAM
Professor Nihal S. de Silva is a Research Scientist and Adjunct
Professor at the Washington University, Danforth Campus and Caretech
Labs, USA, who is currently in Sri Lanka to share his expertise on the
prevention of non-communicable diseases with health professionals and
researchers in the country. He has had a long and distinguished career
of research and lecturing in various disciplines of science, in the USA.
His primary areas of expertise are in Biochemistry, Nutrition and
Immunology.
 |
|
Professor
Nihal S. de Silva |
Excerpts of an interview he had with the Sunday Observer.
Question: We understand you are here in an official capacity. What
exactly is the purpose of your visit?
Answer: When President Rajapaksa was recently in the US, he had asked
for help in combating the rise of non-communicable diseases in Sri Lanka
from US Scientists. When I came to hear of it, I immediately volunteered
my services to the Sri Lankan embassy in the US. I am currently working
with the Medical Research Institute and the Health Ministry here, to see
what can be done about the issue.
My visit is being sponsored by the Sri Lankan Embassy in the USA.
When I heard they wanted help back here, I volunteered my services.
Q: Are non-communicable diseases a major problem in Sri Lanka
now?
A: They are on the rise. With changing lifestyles will come
such problems as diabetes and hypertension. The fast food culture has
crept into Sri Lanka now. Falling prey to it is not the best idea for
people who wish to be health conscious. It is a major factor in the rise
of NCDs (Non- Communicable Diseases) the world over.
Q: And what can be done to prevent this?
A: That is the key word. Prevention! Prevention is better than
cure. So people have to take care of their bodies; have a balanced diet.
Exercise regularly - and make sure it's vigorous exercise. Cricket may
be a good sport but it's rather slow. I would recommend activities like
tennis, basketball, soccer or at least fast walking as exercise.
Q: What constitutes a balanced diet?
A: It can be divided by calories. In this country, an average,
healthy person should take in about 1500 - 2000 calories. The saturated
fat concentration of this should be reduced to 10 - 15 percent. Proteins
should go up to 20 percent. The country is surrounded by fish. Fish is
ideal as protein food. Also lentils. If you want more proteins, go
lentils.
The rest of the calorie intake should be carbohydrates. And of
course, it is essential to have a complete supplement of vitamins and
minerals. For example, vitamin D - people should be taking 2000
international units of vitamin D. People in the West get only 50 through
sun light, supplementation is needed. Aging people need 5000 units.
Vitamin D is a hormone. We have 27 000 - 30 000 genes in our body and
according to research done on genomes, Vitamin D has the power to
influence 3000 genes.
Q: Does heredity play a part in non-communicable diseases such
as hypertension and diabetes?
A: It is not your genes, it is modification of your genes by
environmental factors. 'Its called epigenomes or epigenetics. It's not
only your genes that matter but also the effect of environmental factors
on the gene expression that finally determines your health and disease'.
NCDs such as cancer, vascular diseases, pulmonary diseases, hypertension
and diabetes all stem from environmental components. Whether a person is
prone to or is actually suffering from a disease can best be identified
by bio markers.
Q: What are bio markers?
A: Some component of your blood or other body fluids / tissues
that indicates some sort of abnormality. For example, glucose in the
urine indicates diabetes and homocysteine, an amino acid found in blood
indicates heart disease conditions.
 I am currently working on a new technique of diagnosis using these
bio markers. It's called Raman Spectroscopy and it is being used to
diagnose a variety of chronic as well as non-communicable diseases. I am currently working on a new technique of diagnosis using these
bio markers. It's called Raman Spectroscopy and it is being used to
diagnose a variety of chronic as well as non-communicable diseases.
The plus point of the technique is that it is non-invasive; unlike
X-Rays and MRIs, it will not cause any harm to the body. 'I am a pioneer
in this direction and was the first to use it for the
Bronchalveolar lavage fluid of the lung!! this paper was published in
Spectroscopy magazine in 1999-2000!'
Q: What exactly is Raman Spectroscopy and how does it work?
A: It is a laser based photonic technique, using the
wavelength 785 nm. It gives a vibrational fingerprint of the condition
of your cells so that any variation from that of an ideal healthy body
could be detected. Now in the West, it is used in the screening of
cancer, dental problems, lung diseases, heart diseases and even
diabetes.
Right now bio markers such as phlegm, saliva or blood samples are
used but over the next five years I anticipate that it could be used on
the body itself by developing fibre optic cables.
Traditional histopathologic techniques will be replaced by the Raman
Spectroscopy technique soon.
Q: Is it important to eat only organic food?
A: Organic food is costly. So far there is nothing to indicate
that biotechnology of food is harmful. I have been eating corn flakes,
made from bio-tech corn for a number of years now. Nothing has happened
to me. In Europe, they have dubbed this Franken Food, after the human
made monster Frankenstein. They are crazy. People are always wary of
something new.
Research and development is important and I think it ought to be
given a very high priority in Sri Lanka with all our major crops. It
will only be to their ultimate good. It will also create many job
opportunities for young people.
Also our system of herbal medicine should be researched more. The
herbal industry is a billion dollar market in the West now.
Q: Do you believe in herbal medicine?
A: Yes, of course. When we were small, our elders used to tell
us to eat Gotu kola if we wanted to be good in mathematics. Now
scientific research has found that it contains a high amount of
phospholipids which are good for the brain. Gotu Kola is now available
in pill form in the West.
We should do more research into the scientific properties of our
herbs as well as the knowledge that herbal medicine has to impart and
market it properly. This will open up avenues for revenue as well as
employment.
Q: Our Immune system plays a critical role in our health and
dieases. So do Plant nutrients (Phytonutrients or Phytochemicals) have a
role to play in our immune defense?
A: Definitely its an YES! by my research and others in this
very exciting field of study! thats why Ayurvedic herbs have a great
role to play in the immune defense. that's the important Preventive
Strategies we should do in SL, a small country with less money to spend
on health care! unlike the West. which today has realized its mistake
and clamping down the billion dollar health bill! In addition, we are
blessed with a lot of fish. We ought to analyse the oils in the fish to
see if we can extract Omega 3 fatty acids from them. It is a necessary
diet supplement and is currently extracted mostly from plants.
If we do some proper research and analysis, we might be able to
extract and market Omega 3 fatty acids from our fish. The country has a
lot of natural resources but careful planning is needed to make the best
possible use of it. 'Biomedical and Agro-Biotech, both have to go
together to get the best effect for this country! also give employment
for the young people of the North, East, West and South!'
Q: Any other advice for our fellow countrymen?
A: Prevention is better than cure. But once ill, it should be
remembered that people are individuals and should be treated
individually. We all have different genetic make-ups, lifestyles, habits
and environments and these should be taken into account in treatments.
Local medical industry to the fore:
Rubella vaccination saves lives
by Nilma DOLE
Vaccinations have been regarded as medical necessities we can't live
without but also intricate consequences that could happen when we tamper
with Mother Nature. While we're been given the gift of overcoming the
world's deadliest of diseases, we should be cautious that every positive
comes with its share of negatives. So we should not only survive it out
there in a world full of calamities when Pandora opened her box but also
cringe our faces when we get that mild injection as a child.
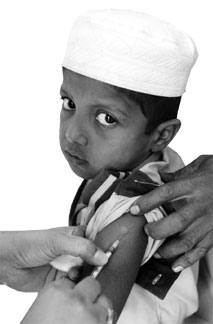
|
Symptoms of rubella
virus infection |
| 1. Appearance of a rash (exanthem) on the face which spreads to the
trunk and limbs and usually fades after three days
2. Low grade fever
3. Swollen glands
4. Joint pains
5. Headache
6. Conjunctivitis. |
According to epidemiologists, a vaccination is the basically
weakened, killed or inactive germs or pathogens that come in the form of
bacteria or viruses which could even be proteins that have been enhanced
to protect the recipient.
Helm
Either way, vaccination treatments have been at the helm of
controversies due to various disputes as experts have been debating
scientific, ethical, political, medical safety, religious and even
highlighting adverse effects making them a force to reckon with.
Countries such as the United States even have National Vaccine Injury
Compensation Program to help those who are harmed and suffer as a result
of vaccinations.
In Sri Lanka, vaccinations began in 1951 when infected cases such as
poliomyelitis, pertussis and tetanus began cropping up significantly. It
was then that the Epidemiological Unit was established in 1959 with
supervision from the World Health Organization (WHO) to survey
communicable diseases.
Dr. Ananda Amarasuriya, Assistant Epidemiologist at the
Epidemiological Unit, said, "Sri Lanka is one of the first among
developing countries globally to introduce a vaccine safety surveillance
system." He said that all reported cases are investigated at different
levels according to the severity of the disease, including Adverse
Events Following Immunisation (AEFI) with follow-ups done from the
grass-root to top level.
What we fail to understand as parents of children is what exactly we
know about vaccinations Dr.Sudath Peiris, another reputed
epidemiologist, said that Sri Lanka has a high literacy rate and
efficient primary health care so naturally, the word about immunisation
gets about. "While 1.8 percent of information about immunisation methods
are given by the media, about 22 percent is given by a paediatrician
where parents rely on their source," he said. Moreover, when reliable
sources talk about immunisations, they project the big picture of deadly
symptoms and conditions of disease as opposed to a simple injection for
the child to prevent such diseases and you can see the results openly.
Adverse
|
Symptoms of Congenital rubella syndrome
|
| 1.Intrauterine infection by Rubella virus and comprises cardiac,
cerebral, ophthalmic and auditory defects.
2. May also cause prematurity
3. Low birth weight
4. Neonatal thrombocytopenia
5. Anaemia
6. Hepatitis
7. If the baby survives the infection, it can be born with severe
heart disorders (PDA being the most common), blindness, deafness, or
other life threatening organ disorders. |
However, about two years ago when 3-year old Asanthi Wasana and
12-year old Peshala Hansini died due to the adverse effects of rubella
which was a simple allergy, people didn't hear from it in a long time.
"So the media sensationalised reporting and then started attacking the
health system and went so far as to create a fear among the public when
they were asked to bring their children to be immunised," he said.
Rich people immediately turned to the private hospitals thinking that
the services and quality of the vaccines would be better thereby
creating a sort of image that the "Those who were poor would reluctantly
and fearfully take their children to the general hospitals," he said.
Studies showed that there were no cases in 2007 but following the media
controversy, there was a sudden outbreak where two cases were reported
in 2008, three cases in 2009 and five cases last year.
"The trend shows that there might be a deadly outbreak of the disease
if we don't educate the public not to believe fake media reporting and
talk to the doctors to see what kind of immunisation is appropriate for
their child. We are here 24 hours of the day, 365 days of the week for
queries and advice with regard to vaccinations," said Dr. Peiris.
So we should stop rubella by trusting our local medical industry
because Sri Lanka is the best country for children to be immunised.
GM lab creates chicken that cannot spread bird flu
by Steve Connor
Norrie Russell, courtesy of Valerie White and The Roslin Institute
Scientists have developed a way of curbing the spread of avian flu with
the help of genetically modified chickens that do not spread the virus.
 |
|
The GM rooster could be the first of
many such disease-resistant animals Getty Images |
The chickens have an extra piece of DNA inserted into their genomes
which produces a “decoy” molecule that blocks the replication of the
influenza virus and prevents transmission to the rest of the flock.
Researchers believe the breakthrough could eventually lead to the
creation of GM poultry, pigs and other livestock that are fully
resistant to a range of infectious diseases. They also said that the
development could help to lower the risk of transmitting dangerous
animal viruses to humans.
While consumers in Britain have been resistant to plant-based
products containing GM ingredients, the scientists behind the GM chicken
believe that the proposal to develop disease-resistant varieties might
become acceptable due to concerns about animal welfare and the
transmission of infections to humans. Laurence Tiley of Cambridge
University, who was a key member of the research team, said: “We believe
the attitude of the UK public to GM food depends on the nature and
purpose of the genetic modification.
“Disease resistance is clearly a beneficial characteristic for animal
welfare and public health.”
The GM chicken was created by adding a synthetic fragment of DNA to
their chromosomes, which causes the chickens to manufacture small
lengths of RNA, the genetic molecule used by influenza viruses.
These particular pieces of RNA act as decoys by locking on to the
enzyme used by flu viruses to make copies of themselves.
“The decoy mimics an essential part of the flu virus genome that is
identical for all strains of influenza A.
“We expect the decoy to work against all strains of avian flu and
that the virus will find it difficult to evolve to escape the effects of
the decoy. If you’ve got genetically modified chickens that are
resistant to the avian flu virus then you don’t in theory have to bother
with vaccination anymore,” he added. When scientists carried out tests
on the GM chickens they found that although the birds were still
vulnerable to being infected with avian flu and that they became sick
with flu, but they did not appear to transmit the virus to other members
of their flock, even if these birds were normal, non-GM varieties.
Helen Sang of the Roslin Institute at Edinburgh University, another
leading member of the team that carried out the study, published in the
journal Science, said that the results achieved so far are “very
encouraging”.
Courtesy: The Independent
|

