Shared inequalities: at work and at home
Just as women face challenges in participating in the work domain, so
men face challenges participating in the home domain.
Emma Watson in her much-discussed UN speech observed that
inequalities faced by women are everyone’s problem, and importantly,
they are only a part of the problem.
Just as inequalities are overlooked, so too are the solutions.
Annabel Crabb recently observed that career women are frequently asked
about how they manage their family lives while men never are.
Her solution is deceptively simple: “I don’t think the answer is to
stop asking women. The answer is to start asking men.”
How are you managing your home life?
This question offers more than a promise of equal treatment of
working women and men. It also draws attention to the need for work at
home.
Unpaid household work is estimated to be equivalent to 50% of GDP.
Who does this work? Women do. At a rate almost two times that of men and
even greater if they have children.
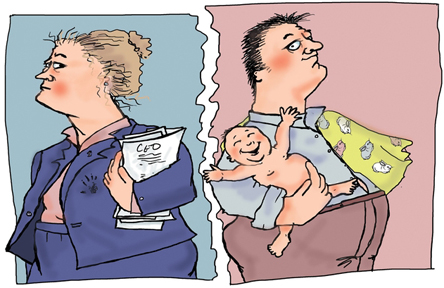 However,
while women do about two-thirds of the unpaid household work, men do
about two-thirds of the paid work. These ratios have changed little in
the last decade, suggestive of a norm. However,
while women do about two-thirds of the unpaid household work, men do
about two-thirds of the paid work. These ratios have changed little in
the last decade, suggestive of a norm.
What little change has been observed is women entering the workforce
rather than men leaving. Work at home still needs to be done leading to
what Crabb dubs The Wife Drought.
Hazards of paid work
Paid work offers attractive benefits, but it also has costs. Work is
harmful to health and safety.
Men have higher rates of the work-related injuries, partly due to
their job choices and higher participation.
And whether related to their greater engagement with the public
sphere or not, men also experience higher rates of victimisation by
crime, suicide and earlier death.
So why are men not leaving the work place simultaneously easing his
own burden at work and a woman’s burden at home? Well, fathers who might
most qualify for this job-swap face mixed signals.
No exit from work, no entry to home
While data show there has been a marked increase in stay-at-home
fathers in the US over two decades, this growth is from a small base
having little impact on male participation at work.
Fathers are given little encouragement as people place less value on
fathers-at-home than mothers. Various sources suggest that men are even
discouraged from engaging in activities related to children.
Charles Areni and I in our book The Other Glass Ceiling provide other
instances: a dad shopping for his daughter’s undies is deemed a security
risk; a single father searching for an au pair is suspicious.
Invisible barriers
Social norms are powerful and continue to operate against both men
and women. Consider the following two scenarios we presented to people
in some research:
“Chris is a single parent of two, a seven-year-old boy and a
three-year old girl, and also the director of marketing for a
medium-sized electronics firm. Today, Chris is scheduled to present key
results from the quarterly sales report to the Board of Trustees but
arrives for the meeting 15 minutes late due to having to drop the older
boy at school, and the younger girl at day care.
In addition to dishevelled hair, there is a noticeable stain down the
left side of Chris’ suit, the result of the young girl vomiting at the
end of her car trip after a hurried breakfast.”
“Terry is a single parent to a four-year-old, James. James spends
some of his time with Terry and some with his other parent. Today, three
police-officers and two child-safety officers have just arrived
unannounced at Terry’s home.
The child-safety officers indicate that specific allegations have
been made that Terry has been abusing James. They insist on entering the
house to interview first Terry, and then James. While the accusations
have been made anonymously, it is perhaps significant to note that the
separation of James’ parents was acrimonious.”
Our research shows that 95% of people presume that Chris in the first
scenario is a woman, and 82% presume that Terry in the second is a
man.However, the gender was not stated in either scenario. It appears
that we associate the failures with gender-role reversals, even if
unconsciously.
Family as a social support system
For better or worse, our social systems are highly specialised with
roles in the home and family remaining relatively unchanged.
Gender role specialisation is changing, but slowly. The participation
by women at work and men at home are increasing as roles are apparently
more negotiated than presumed. Perhaps a limiting factor is that
complete equality may be unattainable. While greater male-involvement at
home could reduce the child-rearing burden faced by women, he cannot
reduce a woman’s burden - and privilege - of being able to bear a child
(as attested to by Monty Python).
In the working domain, progress is made as we see men letting go and
women stepping up. This effort can be complemented in the home domain
with fathers stepping up and mothers letting go. |

