Periodic Table of Elements
 The
periodic table is the most important reference a chemist has, because it
puts all the known elements into a meaningful pattern. The
periodic table is the most important reference a chemist has, because it
puts all the known elements into a meaningful pattern.
Elements are arranged from left to right and top to bottom, in the
order of increasing atomic number. This order generally goes with
increasing atomic mass.
The different rows of elements are called periods. The period number
of an element signifies the highest energy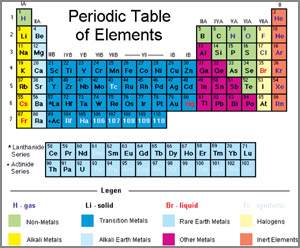 level an electron in that element occupies (in the unexcited state).
level an electron in that element occupies (in the unexcited state).
The number of elements in a period increases as one moves down the
periodic table because as the energy level of the atom increases, the
number of energy sub-levels per energy level increases.
In 1869, the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noted that the
repeating patterns of behaviour could be arranged in a sequence of
elements. This led to the first periodic table of elements.Although
Mendeleev is often considered as the 'father' of the periodic table',
the work of many scientists contributed to its present form.
By 1869, a total of 63 elements had been discovered and as the number
of known elements grew, scientists began to recognise patterns in
properties and began to develop classification schemes.Law of Triads was
the method used by Johann Dobereiner in 1817.
Later, an English chemist introduced the Law of Octave as another
method of classifying the elements.
 The
last major changes to the periodic table resulted from Glenn Seaborg's
work in the middle of the 20th Century. Starting with his discovery of
Plutonium in 1940, he discovered all the transuranic elements (group of
radioactive elements whose atoms are heavier than those of uranium) from
94 to 102. The
last major changes to the periodic table resulted from Glenn Seaborg's
work in the middle of the 20th Century. Starting with his discovery of
Plutonium in 1940, he discovered all the transuranic elements (group of
radioactive elements whose atoms are heavier than those of uranium) from
94 to 102.
He reconfigured (rearranged) the periodic table by placing the
actinide series below the lanthanide series.
In 1951, Seaborg was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his
work. Element 106 has been named Seaborgium (Sg) in his honour.
Law of Triads
When elements are placed in the ascending order of atomic masses,
groups of three elements having similar properties are obtained. The
atomic mass of the middle element of the triad is equal to the
mean(average) of the atomic masses of the other two elements of the
triad.
Law of Octaves
When elements are placed in increasing order of atomic masses, the
properties of the eight elements are
|

Dmitri Mendeleev |
repeated.
Compiled by Janani Amarasekara
****
Science vocabulary
Velocity - The speed of an
object in a particular direction.
Microscope - An optical
instrument that uses a combination of lenses to produce magnified images
of very small objects.
Orbit - The path an object
follows as it travels around another object.
Pole - The place on a
magnet where the magnetic field is strongest.
Prototype - An original
specimen that serves as a model for later examples.
Convection - The
transportation of heat from one place to another by the movement of a
liquid or gas. (A classroom is warmed by a hot air blower due to
convection).
Cryogenics - The science
of very low temperatures, far below the freezing point of water.
Theory - A general
principle that explains or predicts facts or events.
Voltage - Electrical force
or pressure (measured in volts). |
