Muscle relaxation can beat tension
By Lional Wijesiri
These are incredible times to be living in, and technologies such as
computers, televisions, telephones, and cars have made life so much
easier and convenient. Times of tremendous growth and prosperity also
require that you grow and adapt with them. Sometimes it is difficult to
keep up with such a fast-paced and ever changing society, so it is very
important to learn and utilise skills that will help you succeed in the
21st century. These skills will not only help you gain control of your
life, but they will also help you gain that extra advantage needed to
make it in today’s global world.
|

If you do the muscle exercises well, you will find a
pleasant change towards serenity creeping up on you. |
One of the skills that is highly important to learn and implement
into your daily life is relaxation. For many of us, relaxation means
zoning out in front of the TV at the end of a stressful day. But this
does little to reduce the damaging effects of stress. To effectively
combat stress, we need to activate the body’s natural relaxation
response.
Stress and nervous system
However, stress is necessary for life. You need stress for
creativity, learning, and your very survival. Stress is only harmful
when it becomes overwhelming and interrupts the healthy state of
equilibrium that your nervous system needs to remain in balance.
Unfortunately, overwhelming stress has become an increasingly common
characteristic of contemporary life. When stressors throw your nervous
system out of balance, a good relaxation techniques can bring it back
into a balanced state by producing a state of deep calmness.
When stress overwhelms your nervous system your body is flooded with
chemicals that prepare you for “fight or flight.” While the stress
response can be lifesaving in emergency situations where you need to act
quickly, it wears your body down when constantly activated by the
stresses of everyday life.
A good relaxation technique puts the brakes on this heightened state
of readiness and brings your body and mind back into a state of
equilibrium.
There is no single relaxation technique that is best for everyone.
When choosing a relaxation technique, consider your specific needs,
preferences, fitness level, and the way you tend to react to stress.
The right relaxation technique is the one that resonates with you,
fits your lifestyle, and is able to focus your mind and positively
interrupt your everyday thoughts.
Progressive Muscular Relaxation
There are countless techniques used to achieve relaxation, but one of
the procedures that is most commonly practised in the clinical setting
is Dr. Jacobson’s Progressive Muscular Relaxation. It is popular because
of its simplicity and effectiveness.
Progressive Muscular Relaxation technique was developed by American
physician Edmund Jacobson in the early 1920s. The technique involves
learning to monitor tension in each specific muscle group in the body by
deliberately inducing tension in each group. This tension is then
released, with attention paid to the contrast between tension and
relaxation. These learning sessions are not exercises or self-hypnotism.
In his book, Progressive Relaxation, Dr Edmond Jacobson describes how
he first used progressive relaxation techniques with patients who
appeared physically tense. He discovered that he could induce
nerve-muscle relaxation through progressive relaxation – a process of
tensing and relaxing different muscle groups.
Dr Jacobson devoted his life to solve the stress problem. And from
his mass of scientific information obtained through decades of research,
he concluded that it is possible for nearly anyone to (1) go about the
day calmly and as “loose” as a champion athletic and (11) induce at will
the serene repose of untroubled sleep.
It is possible without using drugs or any other means except a simple
physical skill - removal of tension by progressively relaxing muscles.
What Dr. Jacobson learned is that an inner tension depends for its
survival on existing in a “vicious circle.”
The circle may begin with fear, anxiety or over-stimulation, which
then builds the rest of it –including perhaps such elements as
frustration, sleeplessness, fatigue, anger, and ulcers. But one part of
the circulation that is always there is muscle tension. Get rid of
muscle tension and the rest of the elements evaporate.
Muscle control
Briefly put, this is how the Progressive Muscle Relaxation Technique
works:
Step 1: Tension - Inhale and purposely tense up or tighten hard the
selected muscle group (not so hard that you strain). Hold the muscle
tension for 5-10 seconds.
Step 2: Relax - Exhale while quickly but gently letting go, releasing
tension. Take pleasure in the sensation of tension draining out of your
body. Be still 15-20 seconds before moving on to the next muscle group.
Compare relaxation vs. contraction.
Throughout the exercise, you must maintain awareness on how your
muscles feel during both contracting and relaxing. When your attention
wanders, bring it back to the particular muscle group you’re working on.
Alternate muscle groups - from right to left, starting with the
hands, and work up to the shoulders. Then begin with the feet. Starting
with the right foot, work back up to the shoulders (again), leaving the
neck and face last.
|
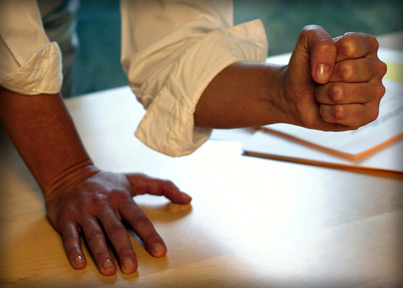
Make a tight fist and note the sensation. That is muscle
tension |
Any particular sequence is in order, but to start with areas in which
physical and emotional tension seem to gather, such as the shoulders,
neck and face might prove difficult.
For example, hands and forearms - clench your hand and make a tight
fist: Upper arms - curl your arm and flex your bicep as if “making a
muscle”: Shoulders - shrug both your shoulders trying to touch them to
your ears: Feet - flex your toes upward: Front of legs - point your toes
so that your foot is parallel with your leg: Back of legs - flex your
feet upwards, stretching your heels down: Thighs - extend your leg
keeping your foot relaxed, press the back of your knee towards the
floor: Abdomen - hold your stomach muscles in tight: Lower Back - press
the small of your back into the chair or floor: Upper Back – (1) with
both arms down along your sides, tighten and press them in against your
body: Chest - breathe in, hold your breath and tighten your chest
muscles.
Shoulders - breath in, hold your breath and again shrug your
shoulders as if trying to touch them to your ears.
Neck - (1) stretch your head back, as if touching your chin to the
ceiling. (2) bend your head forward reaching your chin toward your
chest.
Face - frown, scrunch face and make a stiff “pucker” with your lips,
shutting eyes tight.
Relax
When you have finished your Progressive Muscle Relaxation session,
remain quiet with eyes closed for a few seconds. Mentally scan your body
for any residual tension. If a particular area remains tense, repeat one
or two tense-relax cycles for that group of muscles.
On conclusion take a deep breath, hold it and say to yourself, “I’m
calm” as you slowly exhale. Repeat. Open your eyes and give yourself a
few more seconds to adjust before slowly getting up.
Notice how calm you are. The Progressive Muscle Relaxation method
will enable you to recognise what it actually feels like to be deeply
physically relaxed. You can then wilfully - anytime, anywhere - initiate
physical muscle relaxation at the first signs of any tension. Cherish
this sense of well-being throughout your entire body!
A bit of advice - before practising Progressive Muscle Relaxation,
you should first consult your physician about any deliberate muscle
tensing that may aggravate a pre-existing condition. |

