 How
transfer of heat happens How
transfer of heat happens
In our previous "The World of Science" page, we wrote about some
different types of thermometers, which are all used to measure
temperature. In order to measure our body temperature, our body heat
must transfer to the thermometer bulb. So, how does this heat transfer
happen?
For the transfer of heat to be possible in a system, there should be
a temperature difference in the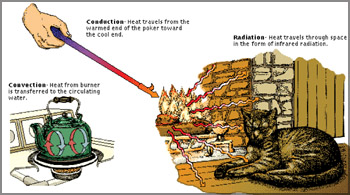 system; heat is always moving from high
to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is known
as the heat source. The area where the temperature is lower is the
heat
sink. system; heat is always moving from high
to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is known
as the heat source. The area where the temperature is lower is the
heat
sink.
When examining systems, scientists measure a number called the
temperature gradient. It is the change in
temperature divided by the
distance. The units are degrees per centimetre. If the temperature is
dropping over a specific distance, the gradient is a negative value. If
the temperature goes up, it is a positive value.
When you touch a surface, how can you tell whether it is hot or cold?
The temperature of that surface must first transfer to your skin. Then
you can say what you feel. When your mother is cooking, if the heat does
not transfer to the pots, how can she warm them up and cook? Of course,
it is all thanks to the transfer of heat. Do you know the ways in which
heat is transferred?
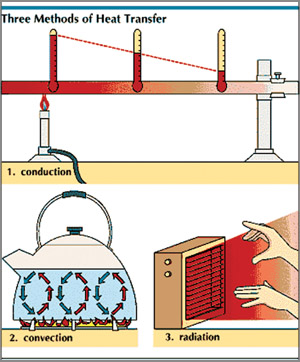
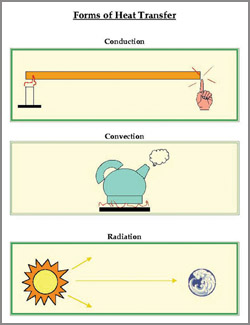
Convection
Convection is the way heat is transferred from one area to another
when there is a "large movement of matter". It is the movement of huge
amounts of an object, taking the heat from one area and placing it in
another. Warm air rises and cold air replaces it. The heat has moved.
Therefore, it is the transfer of heat by motion of objects. When an
area of hot water rises to the top of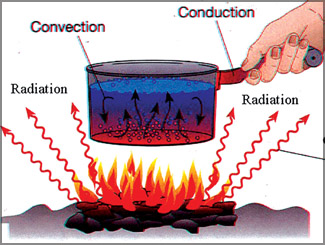 a pot and gives off energy, that
is convection. Another example is, warm air in the atmosphere rising and
giving off energy. The thing to remember is that the object moves. a pot and gives off energy, that
is convection. Another example is, warm air in the atmosphere rising and
giving off energy. The thing to remember is that the object moves.
Radiation
Heat transfer by radiation happens when a temperature gradient exists
and the transfer of energy happens without a conductive medium. That
means, there is no matter there for the heat to pass through.
Radiation is the energy carried by electromagnetic waves (light).
Those waves could be radio waves, infrared, visible light, UV or Gamma
rays. Radiation is usually seen in the red and infrared sections of the
EM spectrum.
In addition, if the temperature of an object doubles (in Kelvin), the
thermal radiation increases 16 times. Therefore, if it goes up four
times, it increases to 32 times the original level.
  Scientists have also discovered that objects that are good at giving
off thermal radiation are also good at absorbing the same energy.
Usually the amount of radiation given off by an object depends on the
temperature. The rate at which you absorb energy depends on the energy
surrounding you. Scientists have also discovered that objects that are good at giving
off thermal radiation are also good at absorbing the same energy.
Usually the amount of radiation given off by an object depends on the
temperature. The rate at which you absorb energy depends on the energy
surrounding you.
Conduction
This is a situation where the heat source and heat sink are
connected. As we discussed before, the heat flows from the source, down
the temperature gradient, to the sink. It is different from convection
because there is no movement of large amounts of matter. The source and
the sink are connected.
Conduction is special as it needs more
free
energy than the others,
for transferring thermal energy. If you touch an ice-cream cone, the
ice-cream heats up because you are a warmer body. If you lie on a hot
sidewalk, the energy moves directly to your body by conduction.
When scientists studied good thermal radiators, they discovered that
good thermal conductors are suitable for conducting electricity. So when
you think of a good conductor, think of gold, silver and platinum.
Janani Amarasekara |
